- World War I; Clockwise from the top: The aftermath of shelling during the Battle of the Somme, Mark V tanks cross the Hindenburg Line, HMS Irresistible sinks after ...
- Find out more about the history of World War I History, including videos, interesting articles, pictures, historical features and more. Get all the facts on HISTORY.com
- World War I was one of the great watersheds of 20th-century geopolitical history. It led to the fall of four great imperial dynasties (in Germany, Russia, Austria ...
- World War I was an extremely bloody war that engulfed Europe from 1914 to 1919, with huge losses of life and little ground lost or won. Fought mostly by soldiers in ..."World War One", "Great War", "WW1", "First World War", and "WWI" redirect here. For the album by White Whale, see WW1 (album). For other uses, see World War One (disambiguation) and Great War (disambiguation).
World War I 
Clockwise from the top: The aftermath of shelling during the Battle of the Somme, Mark V tanks cross the Hindenburg Line, HMS Irresistible sinks after hitting a mine in the Dardanelles, a British Vickers machine gun crew wears gas masks during the Battle of the Somme, Albatros D.III fighters of Jagdstaffel 11Date 28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918
(4 years, 3 months and 2 weeks)Location Europe, Africa, the Middle East, the Pacific Islands, China, Indian Ocean, and off the coast of South and North America Result Allied victory
- Fall of the German, Russian, Ottoman, and Austro-Hungarian empires
- Formation of new countries in Europe and the Middle East
- Transfer of German colonies and regions of the former Ottoman Empire to other powers
- Establishment of the League of Nations. (more...)
Belligerents Allied Powers
 France
France
 British Empire
British Empire
 Russian Empire (until 1917)
Russian Empire (until 1917)
 Serbia
Serbia
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Belgium
Belgium
 Japan
Japan
 Italy (1915–18)
Italy (1915–18)
 Portugal (1916–18)
Portugal (1916–18)
 Romania (1916–18)
Romania (1916–18)
 Hejaz (1916–18)
Hejaz (1916–18)
 United States (1917–18)
United States (1917–18)
 Greece (1917–18)
Greece (1917–18)
 Siam (1917–18)
Siam (1917–18)
...and othersCentral Powers
 Germany
Germany
 Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
 Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
 Bulgaria (1915–18)
Bulgaria (1915–18)
 Azerbaijan (1918[1])
Azerbaijan (1918[1])
 Jabal Shammar (1915–18)
Jabal Shammar (1915–18)
 Dervish State (1914–18)
Dervish State (1914–18)
 Darfur (1915-1916)
Darfur (1915-1916)
...and co-belligerentsCommanders and leaders Allied leaders
 Georges Clemenceau
Georges Clemenceau
 Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Poincaré
 H. H. Asquith
H. H. Asquith
 David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George
 Nicholas II
Nicholas II
 Vittorio Orlando
Vittorio Orlando
 Victor Emmanuel III
Victor Emmanuel III
 Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
 Yoshihito
Yoshihito
 Peter I
Peter I
 Ferdinand I
Ferdinand I
...and othersCentral Powers leaders
 Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II
 Franz Joseph I †
Franz Joseph I †
 Karl I
Karl I
 Mehmed V †
Mehmed V †
 Mehmed VI
Mehmed VI
 Three Pashas
Three Pashas
 Ferdinand I
Ferdinand I
...and othersStrength  12,000,000
12,000,000
 8,841,541[2][3]
8,841,541[2][3]
 8,660,000[4]
8,660,000[4]
 5,615,140
5,615,140
 4,743,826
4,743,826
 1,234,000
1,234,000
 800,000
800,000
 707,343
707,343
 380,000
380,000
 250,000
250,000
 50,000
50,000
Total: 42,959,850[5] 13,250,000
13,250,000
 7,800,000
7,800,000
 2,998,321
2,998,321
 1,200,000
1,200,000
 20,000–25,000
20,000–25,000
 10,000
10,000
 4,000–6,000
4,000–6,000
Total: 25,248,321[5]Casualties and losses Military dead:
5,525,000
Military wounded:
12,831,500
Military missing:
4,121,000
Total:
22,477,500 KIA, WIA or MIA
...further details.Military dead:
4,386,000
Military wounded:
8,388,000
Military missing:
3,629,000
Total:
16,403,000 KIA, WIA or MIA
...further details.
World War I (WWI or WW1), also known as the First World War, the Great War, or the War to End All Wars, was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. More than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, were mobilised in one of the largest wars in history.[6][7] Over nine million combatants and seven million civilians died as a result of the war (including the victims of a number of genocides), a casualty rate exacerbated by the belligerents' technological and industrial sophistication, and the tactical stalemate caused by gruelling trench warfare. It was one of the deadliest conflicts in history, and paved the way for major political changes, including revolutions in many of the nations involved.[8]Events leading to World War I Triple Alliance 1882 Franco-Russian Alliance 1894 Anglo-German naval arms race 1898–1912 Entente Cordiale 1904 First Moroccan Crisis 1905–1906 Anglo-Russian Entente 1907 Bosnian crisis 1908–1909 Agadir Crisis 1911 Italo-Turkish War 1911–1912 Balkan Wars 1912–1913 Assassination of Franz Ferdinand 1914 July Crisis 1914
The war drew in all the world's economic great powers,[9] assembled in two opposing alliances: the Allies (based on the Triple Entente of the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) versus the Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary. Although Italy was a member of the Triple Alliance alongside Germany and Austria-Hungary, it did not join the Central Powers, as Austria-Hungary had taken the offensive, against the terms of the alliance.[10] These alliances were reorganised and expanded as more nations entered the war: Italy, Japan and the United States joined the Allies, while the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria joined the Central Powers.
The trigger for the war was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary, by Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914. This set off a diplomatic crisis when Austria-Hungary delivered an ultimatum to the Kingdom of Serbia,[11][12] and entangled international alliances formed over the previous decades were invoked. Within weeks, the major powers were at war and the conflict soon spread around the world.
On 25 July Russia began mobilisation and on 28 July, the Austro-Hungarians declared war on Serbia. Germany presented an ultimatum to Russia to demobilise, and when this was refused, declared war on Russia on 1 August. Germany then invaded neutral Belgium and Luxembourg before moving towards France, leading the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 4 August.[13][14] After the German march on Paris was halted, what became known as the Western Front settled into a battle of attrition, with a trench line that changed little until 1917. On the Eastern Front, the Russian army was successful against the Austro-Hungarians, but the Germans stopped its invasion of East Prussia. In November 1914, the Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers, opening fronts in the Caucasus, Mesopotamia and the Sinai. In 1915, Italy joined the Allies and Bulgaria joined the Central Powers; Romania joined the Allies in 1916, as did the United States in 1917.
The Russian government collapsed in March 1917, and a revolution in November followed by a further military defeat brought the Russians to terms with the Central Powers via the Treaty of Brest Litovsk, which granted the Germans a significant victory. After a stunning German offensive along the Western Front in the spring of 1918, the Allies rallied and drove back the Germans in a series of successful offensives. On 4 November 1918, the Austro-Hungarian empire agreed to an armistice, and Germany, which had its own trouble with revolutionaries, agreed to an armistice on 11 November 1918, ending the war in victory for the Allies.
By the end of the war or soon after, the German Empire, Russian Empire, Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire ceased to exist. National borders were redrawn, with several independent nations restored or created, and Germany's colonies were parceled out among the victors. During the Paris Peace Conference of 1919, the Big Four (Britain, France, the United States and Italy) imposed their terms in a series of treaties. The League of Nations was formed with the aim of preventing any repetition of such a conflict. This effort failed, and economic depression, renewed nationalism, weakened successor states, and feelings of humiliation (particularly in Germany) eventually contributed to World War II.
Contents
- 1 Names
- 2 Background
- 3 Prelude
- 4 Progress of the war
- 5 Aftermath
- 6 Technology
- 7 War crimes
- 8 Soldiers' experiences
- 9 Support and opposition to the war
- 10 Legacy and memory
- 11 See also
- 12 Footnotes
- 13 Notes
- 14 References
- 15 External links
Names
From the time of its start until the approach of World War II, the First World War was called simply the World War or the Great War and thereafter the First World War or World War I.[15][16] At the time, it was also sometimes called "the war to end war" or "the war to end all wars" due to its then-unparalleled scale and devastation.[17]
In Canada, Maclean's magazine in October 1914 wrote, "Some wars name themselves. This is the Great War."[18] During the interwar period (1918–1939), the war was most often called the World War and the Great War in English-speaking countries.
The term "First World War" was first used in September 1914 by the German biologist and philosopher Ernst Haeckel, who claimed that "there is no doubt that the course and character of the feared 'European War' ... will become the first world war in the full sense of the word,"[19] citing a wire service report in The Indianapolis Star on 20 September 1914. After the onset of the Second World War in 1939, the terms World War I or the First World War became standard, with British and Canadian historians favouring the First World War, and Americans World War I.[20]
Background
Main article: Causes of World War IRival military coalitions in 1914; Triple Entente in green; Triple Alliance in brown. Only the Triple Alliance was a formal "alliance"; the others listed were informal patterns of support.Political and military alliances
During the 19th century, the major European powers went to great lengths to maintain a balance of power throughout Europe, resulting in the existence of a complex network of political and military alliances throughout the continent by 1900.[21] These began in 1815, with the Holy Alliance between Prussia, Russia, and Austria. When Germany was united in 1871, Prussia became part of the new German nation. Soon after, in October 1873, German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck negotiated the League of the Three Emperors (German: Dreikaiserbund) between the monarchs of Austria-Hungary, Russia and Germany. This agreement failed because Austria-Hungary and Russia could not agree over Balkan policy, leaving Germany and Austria-Hungary in an alliance formed in 1879, called the Dual Alliance. This was seen as a method of countering Russian influence in the Balkans as the Ottoman Empire continued to weaken.[10] This alliance expanded in 1882 to include Italy, in what became the Triple Alliance.[22]
Bismarck had especially worked to hold Russia at Germany's side in an effort to avoid a two-front war with France and Russia. When Wilhelm II ascended to the throne as German Emperor (Kaiser), Bismarck was compelled to retire and his system of alliances was gradually de-emphasised. For example, the Kaiser refused, in 1890, to renew the Reinsurance Treaty with Russia. Two years later, the Franco-Russian Alliance was signed to counteract the force of the Triple Alliance. In 1904, Britain signed a series of agreements with France, the Entente Cordiale, and in 1907, Britain and Russia signed the Anglo-Russian Convention. While these agreements did not formally ally Britain with France or Russia, they made British entry into any future conflict involving France or Russia a possibility, and the system of interlocking bilateral agreements became known as the Triple Entente.[10]
SMS Rheinland, a Nassau-class battleship, Germany's first response to Dreadnought.Arms race
German industrial and economic power had grown greatly after unification and the foundation of the Empire in 1871 following the Franco-Prussian War. From the mid-1890s on, the government of Wilhelm II used this base to devote significant economic resources for building up the Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial German Navy), established by Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, in rivalry with the British Royal Navy for world naval supremacy.[23] As a result, each nation strove to out-build the other in capital ships. With the launch of HMS Dreadnought in 1906, the British Empire expanded on its significant advantage over its German rival.[23] The arms race between Britain and Germany eventually extended to the rest of Europe, with all the major powers devoting their industrial base to producing the equipment and weapons necessary for a pan-European conflict.[24] Between 1908 and 1913, the military spending of the European powers increased by 50%.[25]
Sarajevo citizens reading a poster with the proclamation of the Austrian annexation in 1908Conflicts in the Balkans
Austria-Hungary precipitated the Bosnian crisis of 1908–1909 by officially annexing the former Ottoman territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which it had occupied since 1878. This angered the Kingdom of Serbia and its patron, the Pan-Slavic and Orthodox Russian Empire. Russian political manoeuvring in the region destabilised peace accords that were already fracturing in the Balkans, which came to be known as the "powder keg of Europe."[26] In 1912 and 1913, the First Balkan War was fought between the Balkan League and the fracturing Ottoman Empire. The resulting Treaty of London further shrank the Ottoman Empire, creating an independent Albanian state while enlarging the territorial holdings of Bulgaria, Serbia, Montenegro, and Greece. When Bulgaria attacked Serbia and Greece on 16 June 1913, it lost most of Macedonia to Serbia and Greece, and Southern Dobruja to Romania in the 33-day Second Balkan War, further destabilising the region.[27] The Great Powers were able to keep these Balkan conflicts contained, but the next one would spread throughout Europe and beyond.
Prelude
Sarajevo assassination
Main article: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of AustriaOn 28 June 1914, Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand visited the Bosnian capital, Sarajevo. A group of six assassins (Cvjetko Popović, Gavrilo Princip, Muhamed Mehmedbašić, Nedeljko Čabrinović, Trifko Grabež, Vaso Čubrilović) from the Yugoslavist group Mlada Bosna, supplied by the Serbian Black Hand, had gathered on the street where the Archduke's motorcade would pass, with the intention of assassinating him. Čabrinović threw a grenade at the car, but missed. Some nearby were injured by the blast, but Ferdinand's convoy carried on. The other assassins failed to act as the cars drove past them.This picture is usually associated with the arrest of Gavrilo Princip, although some[28][29] believe it depicts Ferdinand Behr, a bystander.
About an hour later, when Ferdinand was returning from a visit at the Sarajevo Hospital with those wounded in the assassination attempt, the convoy took a wrong turn into a street where, by coincidence, Princip stood. With a pistol, Princip shot and killed Ferdinand and his wife Sophie. The reaction among the people in Austria was mild, almost indifferent. As historian Zbyněk Zeman later wrote, "the event almost failed to make any impression whatsoever. On Sunday and Monday (28 and 29 June), the crowds in Vienna listened to music and drank wine, as if nothing had happened.".[30][31] Nevertheless, the political impact of the murder of the heir to the throne was significant and has been described as a "9/11 effect, a terrorist event charged with historic meaning, transforming the political chemistry in Vienna.[32] And although they were not personally close, the Emperor Franz Joseph was profoundly shocked and upset.
The Austro-Hungarian authorities encouraged the subsequent anti-Serb riots in Sarajevo, in which Bosnian Croats and Bosniaks killed two Bosnian Serbs and damaged numerous Serb-owned buildings.[33][34] Violent actions against ethnic Serbs were also organized outside Sarajevo, in other cities in Austro-Hungarian-controlled Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia. Austro-Hungarian authorities in Bosnia and Herzegovina imprisoned and extradited approximately 5,500 prominent Serbs, 700 to 2,200 of whom died in prison. A further 460 Serbs were sentenced to death. A predominantly Bosniak special militia known as the Schutzkorps was established and carried out the persecution of Serbs.[35][36][37][38]
July Crisis
Main article: July CrisisCrowds on the streets in the aftermath of the anti-Serb riots in Sarajevo, 29 June 1914The assassination led to a month of diplomatic manoeuvring between Austria-Hungary, Germany, Russia, France and Britain, called the July Crisis. Believing correctly that Serbian officials (especially the officers of the Black Hand) were involved in the plot to murder the Archduke, and wanting to finally end Serbian interference in Bosnia,[39] Austria-Hungary delivered to Serbia on 23 July the July Ultimatum, a series of ten demands that were made intentionally unacceptable, in an effort to provoke a war with Serbia.[40] The next day, after the Council of Ministers of Russia was held under the chairmanship of the Tsar at Krasnoe Selo, Russia ordered general mobilization for Odessa, Kiev, Kazan and Moscow military districts, and fleets of the Baltic and the Black Sea. They also asked other regions to accelerate preparations for general mobilization. Serbia decreed general mobilization on the 25th and, that night declared that they accepted all the terms of the ultimatum, except article six, which demanded that Austrian delegates be allowed in Serbia for the purpose of participation in the investigation into the assassination. Following this, Austria broke off diplomatic relations with Serbia and, the next day ordered a partial mobilization. Finally, on 28 July 1914, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia.Ethno-linguistic map of Austria-Hungary, 1910. Bosnia-Herzegovina was annexed in 1908.
On 25 July, Russia, in support of its Serb protégé, unilaterally declared – outside of the conciliation procedure provided by the Franco-Russian military agreements – partial mobilization against Austria-Hungary. On the 30th, Russia ordered general mobilization against Germany. German Chancellor Bethmann-Hollweg waited until the 31st for an appropriate response, when Germany declared a "state of danger of war." Kaiser Wilhelm II asked his cousin, Tsar Nicolas II, to suspend the Russian general mobilization. When he refused, Germany issued an ultimatum demanding its mobilization be stopped, and a commitment not to support Serbia. Another was sent to France, asking her not to support Russia if it were to come to the defence of Serbia. On 1 August, after the Russian response, Germany mobilized and declared war on Russia. This also led to the general mobilization in Austria-Hungary on 4 August.
The German government issued demands to France that it remain neutral as they had to decide which deployment plan to implement, it being difficult if not impossible to change the deployment whilst it was underway. The modified German Schlieffen Plan, Aufmarsch II West, would deploy 80% of the army in the west, and Aufmarsch I Ost and Aufmarsch II Ost would deploy 60% in the west and 40% in the east as this was the maximum that the East Prussian railway infrastructure could carry. The French did not respond, but sent a mixed message by ordering their troops to withdraw 10 km (6 mi) from the border to avoid any incidents, and at the same time ordered the mobilisation of her reserves. Germany responded by mobilising its own reserves and implementing Aufmarsch II West. On 1 August Wilhelm ordered General Moltke to "march the whole of the … army to the East" after he had been wrongly informed that the British would remain neutral as long as France was not attacked. The General convinced the Kaiser that improvising the redeployment of a million men was unthinkable and that making it possible for the French to attack the Germans "in the rear" might prove disastrous. Yet Wilhelm insisted that the German army should not march into Luxembourg until he received a telegram sent by his cousin George VI, who made it clear that there had been a misunderstanding. Eventually the Kaiser told Molkte, "Now you can do what you want."[41][42] Germany attacked Luxembourg on 2 August, and on 3 August declared war on France. On 4 August, after Belgium refused to permit German troops to cross its borders into France, Germany declared war on Belgium as well.[43][44][45] Britain declared war on Germany at 19:00 UTC on 4 August 1914 (effective from 11 pm), following an "unsatisfactory reply" to the British ultimatum that Belgium must be kept neutral.[46]
Progress of the war
Opening hostilities
Confusion among the Central Powers
The strategy of the Central Powers suffered from miscommunication. Germany had promised to support Austria-Hungary's invasion of Serbia, but interpretations of what this meant differed. Previously tested deployment plans had been replaced early in 1914, but those had never been tested in exercises. Austro-Hungarian leaders believed Germany would cover its northern flank against Russia.[47] Germany, however, envisioned Austria-Hungary directing most of its troops against Russia, while Germany dealt with France. This confusion forced the Austro-Hungarian Army to divide its forces between the Russian and Serbian fronts.
Serbian campaign
Serbian Army Blériot XI "Oluj", 1915Main article: Serbian Campaign of World War IAustria invaded and fought the Serbian army at the Battle of Cer and Battle of Kolubara beginning on 12 August. Over the next two weeks, Austrian attacks were thrown back with heavy losses, which marked the first major Allied victories of the war and dashed Austro-Hungarian hopes of a swift victory. As a result, Austria had to keep sizable forces on the Serbian front, weakening its efforts against Russia.[48] Serbia's defeat of the Austro-Hungarian invasion of 1914 counts among the major upset victories of the twentieth century.[49]
German forces in Belgium and France
Main article: Western Front (World War I)At the outbreak of World War I, 80% of the German army was deployed as seven field armies in the west according to the plan Aufmarsch II West. However, they were then assigned to execute the retired deployment plan Aufmarsch I West, also known as the Schlieffen Plan. This would march German armies through northern Belgium and into France, in an attempt to encircle the French army and then breach the 'second defensive area' of the fortresses of Verdun and Paris and the Marne river.[11]German soldiers in a railway goods wagon on the way to the front in 1914. Early in the war, all sides expected the conflict to be a short one.
Aufmarsch I West was one of four deployment plans available to the German General Staff in 1914. Each plan favoured certain operations, but did not specify exactly how those operations were to be carried out, leaving the commanding officers to carry those out at their own initiative and with minimal oversight.[clarification needed] Aufmarsch I West, designed for a one-front war with France, had been retired once it became clear it was irrelevant to the wars Germany could expect to face; both Russia and Britain were expected to help France, and there was no possibility of Italian nor Austro-Hungarian troops being available for operations against France. But despite its unsuitability, and the availability of more sensible and decisive options, it retained a certain allure due to its offensive nature and the pessimism of pre-war thinking, which expected offensive operations to be short-lived, costly in casualties, and unlikely to be decisive. Accordingly, the Aufmarsch II West deployment was changed for the offensive of 1914, despite its unrealistic goals and the insufficient forces Germany had available for decisive success.[50] Moltke took Schlieffen's plan and modified the deployment of forces on the western front by reducing the right wing, the one to advance through Belgium, from 85% to 70%. In the end, the Schlieffen plan was so radically modified by Moltke, that it could be more properly called the Moltke Plan.[51]
The plan called for the right flank of the German advance to bypass the French armies concentrated on the Franco-German border, defeat the French forces closer to Luxembourg and Belgium and move south to Paris. Initially the Germans were successful, particularly in the Battle of the Frontiers (14–24 August). By 12 September, the French, with assistance from the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), halted the German advance east of Paris at the First Battle of the Marne (5–12 September) and pushed the German forces back some 50 km (31 mi). The French offensive into southern Alsace, launched on 20 August with the Battle of Mulhouse, had limited success.
In the east, Russia invaded with two armies. In response, Germany rapidly moved the 8th Field Army from its previous role as reserve for the invasion of France to East Prussia by rail across the German Empire. This army, led by general Paul von Hindenburg defeated Russia in a series of battles collectively known as the First Battle of Tannenberg (17 August – 2 September). While the Russian invasion failed, it caused the diversion of German troops to the east, allowing the Allied victory at the First Battle of the Marne. This meant Germany failed to achieve its objective of avoiding a long, two-front war. However, the German army had fought its way into a good defensive position inside France and effectively halved France's supply of coal. It had also killed or permanently crippled 230,000 more French and British troops than it itself had lost. Despite this, communications problems and questionable command decisions cost Germany the chance of a more decisive outcome.[52]
Asia and the Pacific
Main article: Asian and Pacific theatre of World War INew Zealand occupied German Samoa (later Western Samoa) on 30 August 1914. On 11 September, the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force landed on the island of Neu Pommern (later New Britain), which formed part of German New Guinea. On 28 October, the German cruiser SMS Emden sank the Russian cruiser Zhemchug in the Battle of Penang. Japan seized Germany's Micronesian colonies and, after the Siege of Tsingtao, the German coaling port of Qingdao on the Chinese Shandong peninsula. As Vienna refused to withdraw the Austro-Hungarian cruiser SMS Kaiserin Elisabeth from Tsingtao, Japan declared war not only on Germany, but also on Austria-Hungary; the ship participated in the defense of Tsingtao where it was sunk in November 1914.[53] Within a few months, the Allied forces had seized all the German territories in the Pacific; only isolated commerce raiders and a few holdouts in New Guinea remained.[54][55]
African campaigns
Main article: African theatre of World War ISome of the first clashes of the war involved British, French, and German colonial forces in Africa. On 6–7 August, French and British troops invaded the German protectorate of Togoland and Kamerun. On 10 August, German forces in South-West Africa attacked South Africa; sporadic and fierce fighting continued for the rest of the war. The German colonial forces in German East Africa, led by Colonel Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck, fought a guerrilla warfare campaign during World War I and only surrendered two weeks after the armistice took effect in Europe.[56]
Indian support for the Allies
Further information: Hindu–German Conspiracy, Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition, and Third Anglo-Afghan WarGermany attempted to use Indian nationalism and pan-Islamism to its advantage. She tried instigating uprisings in India, and sent a mission to Afghanistan urging her to join the war on the side of Central powers. However, contrary to British fears of a revolt in India, the outbreak of the war saw an unprecedented outpouring of loyalty and goodwill towards Britain.[57][58] Indian political leaders from the Indian National Congress and other groups were eager to support the British war effort, since they believed that strong support for the war effort would further the cause of Indian Home Rule.[citation needed] The Indian Army in fact outnumbered the British Army at the beginning of the war; about 1.3 million Indian soldiers and labourers served in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, while the central government and the princely states sent large supplies of food, money, and ammunition. In all, 140,000 men served on the Western Front and nearly 700,000 in the Middle East. Casualties of Indian soldiers totalled 47,746 killed and 65,126 wounded during World War I.[59] The suffering engendered by the war, as well as the failure of the British government to grant self-government to India after the end of hostilities, bred disillusionment and fuelled the campaign for full independence that would be led by Mohandas K. Gandhi and others.[citation needed]
Western Front
Main article: Western Front (World War I)Trench warfare begins
Military tactics developed before World War I failed to keep pace with advances in technology and had become obsolete. These advances had allowed the creation of strong defensive systems, which out-of-date military tactics could not break through for most of the war. Barbed wire was a significant hindrance to massed infantry advances, while artillery, vastly more lethal than in the 1870s, coupled with machine guns, made crossing open ground extremely difficult.[60] Commanders on both sides failed to develop tactics for breaching entrenched positions without heavy casualties. In time, however, technology began to produce new offensive weapons, such as gas warfare and the tank.[61]Royal Irish Rifles in a communications trench, first day on the Somme, 1916
Just after the First Battle of the Marne (5–12 September 1914), Entente and German forces repeatedly attempted manoeuvring to the north in an effort to outflank each other: this series of manoeuvres became known as the "Race to the Sea". When these outflanking efforts failed, the opposing forces soon found themselves facing an uninterrupted line of entrenched positions from Lorraine to Belgium's coast.[11] Britain and France sought to take the offensive, while Germany defended the occupied territories. Consequently, German trenches were much better constructed than those of their enemy; Anglo-French trenches were only intended to be "temporary" before their forces broke through the German defences.[62]
Both sides tried to break the stalemate using scientific and technological advances. On 22 April 1915, at the Second Battle of Ypres, the Germans (violating the Hague Convention) used chlorine gas for the first time on the Western Front. Several types of gas soon became widely used by both sides, and though it never proved a decisive, battle-winning weapon, poison gas became one of the most-feared and best-remembered horrors of the war.[63][64] Tanks were developed by Britain and France, and were first used in combat by the British during the Battle of Flers–Courcelette (part of the Battle of the Somme) on 15 September 1916, with only partial success. However, their effectiveness would grow as the war progressed; the Allies built tanks in large numbers, whilst the Germans employed only a few of their own design, supplemented by captured Allied tanks.
Continuation of trench warfare
French 87th regiment near Verdun, 1916King George V (front left) and a group of officials inspect a British munitions factory in 1917Neither side proved able to deliver a decisive blow for the next two years. Throughout 1915–17, the British Empire and France suffered more casualties than Germany, because of both the strategic and tactical stances chosen by the sides. Strategically, while the Germans only mounted one major offensive, the Allies made several attempts to break through the German lines.Canadian troops advancing with a British Mark II tank at the Battle of Vimy Ridge, 1917
In February 1916 the Germans attacked the French defensive positions at Verdun. Lasting until December 1916, the battle saw initial German gains, before French counter-attacks returned matters to near their starting point. Casualties were greater for the French, but the Germans bled heavily as well, with anywhere from 700,000[65] to 975,000[66] casualties suffered between the two combatants. Verdun became a symbol of French determination and self-sacrifice.[67]
The Battle of the Somme was an Anglo-French offensive of July to November 1916. The opening of this offensive (1 July 1916) saw the British Army endure the bloodiest day in its history, suffering 57,470 casualties, including 19,240 dead, on the first day alone. The entire Somme offensive cost the British Army some 420,000 casualties. The French suffered another estimated 200,000 casualties and the Germans an estimated 500,000.[68]
Protracted action at Verdun throughout 1916,[69] combined with the bloodletting at the Somme, brought the exhausted French army to the brink of collapse. Futile attempts using frontal assault came at a high price for both the British and the French and led to the widespread French Army Mutinies, after the failure of the costly Nivelle Offensive of April–May 1917.[70] The concurrent British Battle of Arras was more limited in scope, and more successful, although ultimately of little strategic value.[71][72] A smaller part of the Arras offensive, the capture of Vimy Ridge by the Canadian Corps, became highly significant to that country: the idea that Canada's national identity was born out of the battle is an opinion widely held in military and general histories of Canada.[73][74]
The last large-scale offensive of this period was a British attack (with French support) at Passchendaele (July–November 1917). This offensive opened with great promise for the Allies, before bogging down in the October mud. Casualties, though disputed, were roughly equal, at some 200,000–400,000 per side.
These years of trench warfare in the West saw no major exchanges of territory and, as a result, are often thought of as static and unchanging. However, throughout this period, British, French, and German tactics constantly evolved to meet new battlefield challenges.
Main article: Naval warfare of World War IAt the start of the war, the German Empire had cruisers scattered across the globe, some of which were subsequently used to attack Allied merchant shipping. The British Royal Navy systematically hunted them down, though not without some embarrassment from its inability to protect Allied shipping. For example, the German detached light cruiser SMS Emden, part of the East-Asia squadron stationed at Qingdao, seized or destroyed 15 merchantmen, as well as sinking a Russian cruiser and a French destroyer. However, most of the German East-Asia squadron—consisting of the armoured cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau , light cruisers Nürnberg and Leipzig and two transport ships—did not have orders to raid shipping and was instead underway to Germany when it met British warships. The German flotilla and Dresden sank two armoured cruisers at the Battle of Coronel, but was virtually destroyed at the Battle of the Falkland Islands in December 1914, with only Dresden and a few auxiliaries escaping, but after the Battle of Más a Tierra these too had been destroyed or interned.[75]Battleships of the Hochseeflotte, 1917
Soon after the outbreak of hostilities, Britain began a naval blockade of Germany. The strategy proved effective, cutting off vital military and civilian supplies, although this blockade violated accepted international law codified by several international agreements of the past two centuries.[76] Britain mined international waters to prevent any ships from entering entire sections of ocean, causing danger to even neutral ships.[77] Since there was limited response to this tactic of the British, Germany expected a similar response to its unrestricted submarine warfare.[78]
The Battle of Jutland (German: Skagerrakschlacht, or "Battle of the Skagerrak") developed into the largest naval battle of the war. It was the only full-scale clash of battleships during the war, and one of the largest in history. The Kaiserliche Marine's High Seas Fleet, commanded by Vice Admiral Reinhard Scheer, fought the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet, led by Admiral Sir John Jellicoe. The engagement was a stand off, as the Germans were outmanoeuvred by the larger British fleet, but managed to escape and inflicted more damage to the British fleet than they received. Strategically, however, the British asserted their control of the sea, and the bulk of the German surface fleet remained confined to port for the duration of the war.[79]
German U-boats attempted to cut the supply lines between North America and Britain.[80] The nature of submarine warfare meant that attacks often came without warning, giving the crews of the merchant ships little hope of survival.[80][81] The United States launched a protest, and Germany changed its rules of engagement. After the sinking of the passenger ship RMS Lusitania in 1915, Germany promised not to target passenger liners, while Britain armed its merchant ships, placing them beyond the protection of the "cruiser rules", which demanded warning and movement of crews to "a place of safety" (a standard that lifeboats did not meet).[82] Finally, in early 1917, Germany adopted a policy of unrestricted submarine warfare, realising that the Americans would eventually enter the war.[80][83] Germany sought to strangle Allied sea lanes before the United States could transport a large army overseas, but could maintain only five long-range U-boats on station, to limited effect.[80]U-155 exhibited near Tower Bridge in London, after the 1918 Armistice.
The U-boat threat lessened in 1917, when merchant ships began travelling in convoys, escorted by destroyers. This tactic made it difficult for U-boats to find targets, which significantly lessened losses; after the hydrophone and depth charges were introduced, accompanying destroyers could attack a submerged submarine with some hope of success. Convoys slowed the flow of supplies, since ships had to wait as convoys were assembled. The solution to the delays was an extensive program of building new freighters. Troopships were too fast for the submarines and did not travel the North Atlantic in convoys.[84] The U-boats had sunk more than 5,000 Allied ships, at a cost of 199 submarines.[85] World War I also saw the first use of aircraft carriers in combat, with HMS Furious launching Sopwith Camels in a successful raid against the Zeppelin hangars at Tondern in July 1918, as well as blimps for antisubmarine patrol.[86]
Southern theatres
War in the Balkans
Main articles: Balkans Campaign (World War I), Bulgaria during World War I, Serbian Campaign (World War I), and Macedonian FrontFaced with Russia, Austria-Hungary could spare only one-third of its army to attack Serbia. After suffering heavy losses, the Austrians briefly occupied the Serbian capital, Belgrade. A Serbian counter-attack in the Battle of Kolubara succeeded in driving them from the country by the end of 1914. For the first ten months of 1915, Austria-Hungary used most of its military reserves to fight Italy. German and Austro-Hungarian diplomats, however, scored a coup by persuading Bulgaria to join the attack on Serbia.[88] The Austro-Hungarian provinces of Slovenia, Croatia and Bosnia provided troops for Austria-Hungary, in the fight with Serbia, Russia and Italy. Montenegro allied itself with Serbia.[89]Bulgarian soldiers in a trench, preparing to fire against an incoming airplane.
Bulgaria declared war on Serbia, 12 October and joined in the attack by the Austro-Hungarian army under Mackensen's army of 250,000 that was already underway. Serbia was conquered in a little more than a month, as the Central Powers, now including Bulgaria, sent in 600,000 troops total. The Serbian army, fighting on two fronts and facing certain defeat, retreated into northern Albania. The Serbs suffered defeat in the Battle of Kosovo. Montenegro covered the Serbian retreat towards the Adriatic coast in the Battle of Mojkovac in 6–7 January 1916, but ultimately the Austrians also conquered Montenegro. The surviving Serbian soldiers were evacuated by ship to Greece.[90] After conquest, Serbia was divided between Austro-Hungary and Bulgaria.[91]
In late 1915, a Franco-British force landed at Salonica in Greece, to offer assistance and to pressure its government to declare war against the Central Powers. However, the pro-German King Constantine I dismissed the pro-Allied government of Eleftherios Venizelos before the Allied expeditionary force arrived.[92] The friction between the King of Greece and the Allies continued to accumulate with the National Schism, which effectively divided Greece between regions still loyal to the king and the new provisional government of Venizelos in Salonica. After intense negotiations and an armed confrontation in Athens between Allied and royalist forces (an incident known as Noemvriana), the King of Greece resigned and his second son Alexander took his place; Greece then officially joined the war on the side of the Allies.
In the beginning, the Macedonian Front was mostly static. French and Serbian forces retook limited areas of Macedonia by recapturing Bitola on 19 November 1916 following the costly Monastir Offensive, which brought stabilization of the front.[93]
Serbian and French troops finally made a breakthrough in September 1918, after most of the German and Austro-Hungarian troops had been withdrawn. The Bulgarians suffered their only defeat of the war at the Battle of Dobro Pole. Bulgaria capitulated two weeks later, on 29 September 1918.[94] The German high command responded by despatching troops to hold the line, but these forces were far too weak to reestablish a front.[95]
The disappearance of the Macedonian Front meant that the road to Budapest and Vienna was now opened to Allied forces. Hindenburg and Ludendorff concluded that the strategic and operational balance had now shifted decidedly against the Central Powers and, a day after the Bulgarian collapse, insisted on an immediate peace settlement.[96]
Ottoman Empire
Main article: History of the Ottoman Empire during World War ISee also: Middle Eastern theatre of World War IAustralian troops charging near a Turkish trench during the Gallipoli CampaignKaiser Wilhelm II inspecting Turkish troops of the 15th Corps in East Galicia, Poland. Prince Leopold of Bavaria, the Supreme Commander of the German Army on the Eastern Front, is second from the left.The Ottomans threatened Russia's Caucasian territories and Britain's communications with India via the Suez Canal. As the conflict progressed, the Ottoman Empire took advantage of the European powers' preoccupation with the war and conducted large-scale ethnic cleansing of the indigenous Armenian, Greek, and Assyrian Christian populations, known as the Armenian Genocide, Greek Genocide, and Assyrian Genocide.[97][98][99]Russian forest trench at the Battle of Sarikamish, 1914–1915
The British and French opened overseas fronts with the Gallipoli (1915) and Mesopotamian campaigns (1914). In Gallipoli, the Ottoman Empire successfully repelled the British, French, and Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZACs). In Mesopotamia, by contrast, after the defeat of the British defenders in the Siege of Kut by the Ottomans (1915–16), British Imperial forces reorganised and captured Baghdad in March 1917. The British were aided in Mesopotamia by local Arab and Assyrian tribesmen, while the Ottomans employed local Kurdish and Turcoman tribes.[100]
Further to the west, the Suez Canal was defended from Ottoman attacks in 1915 and 1916; in August, a German and Ottoman force was defeated at the Battle of Romani by the ANZAC Mounted Division and the 52nd (Lowland) Infantry Division. Following this victory, an Egyptian Expeditionary Force advanced across the Sinai Peninsula, pushing Ottoman forces back in the Battle of Magdhaba in December and the Battle of Rafa on the border between the Egyptian Sinai and Ottoman Palestine in January 1917.[101]
Russian armies generally saw success in the Caucasus. Enver Pasha, supreme commander of the Ottoman armed forces, was ambitious and dreamed of re-conquering central Asia and areas that had been lost to Russia previously. He was, however, a poor commander.[102] He launched an offensive against the Russians in the Caucasus in December 1914 with 100,000 troops, insisting on a frontal attack against mountainous Russian positions in winter. He lost 86% of his force at the Battle of Sarikamish.[103]
In December 1914 the Ottoman Empire, with German support, invaded Persia (modern Iran) in an effort to cut off British and Russian access to petroleum reservoirs around Baku near the Caspian Sea.[104] Persia, ostensibly neutral, had long been under the spheres of British and Russian influence. The Ottomans and Germans were aided by Kurdish and Azeri forces, together with a large number of major Iranian tribes, such as the Qashqai, Tangistanis, Luristanis, and Khamseh, while the Russians and British had the support of Armenian and Assyrian forces. The Persian Campaign was to last until 1918 and end in failure for the Ottomans and their allies. However the Russian withdrawal from the war in 1917 led to Armenian and Assyrian forces, who had hitherto inflicted a series of defeats upon the forces of the Ottomans and their allies, being cut off from supply lines, outnumbered, outgunned and isolated, forcing them to fight and flee towards British lines in northern Mesopotamia.[105]
General Yudenich, the Russian commander from 1915 to 1916, drove the Turks out of most of the southern Caucasus with a string of victories.[103] In 1917, Russian Grand Duke Nicholas assumed command of the Caucasus front. Nicholas planned a railway from Russian Georgia to the conquered territories, so that fresh supplies could be brought up for a new offensive in 1917. However, in March 1917 (February in the pre-revolutionary Russian calendar), the Czar abdicated in the course of the February Revolution and the Russian Caucasus Army began to fall apart.
The Arab Revolt, instigated by the Arab bureau of the British Foreign Office, started June 1916 with the Battle of Mecca, led by Sherif Hussein of Mecca, and ended with the Ottoman surrender of Damascus. Fakhri Pasha, the Ottoman commander of Medina, resisted for more than two and half years during the Siege of Medina before surrendering.[106]
The Senussi tribe, along the border of Italian Libya and British Egypt, incited and armed by the Turks, waged a small-scale guerrilla war against Allied troops. The British were forced to dispatch 12,000 troops to oppose them in the Senussi Campaign. Their rebellion was finally crushed in mid-1916.[107]
Total Allied casualties on the Ottoman fronts amounted 650,000 men. Total Ottoman casualties were 725,000 (325,000 dead and 400,000 wounded).[108]
Italian participation
Main articles: Italian Front (World War I) and Albania during World War IFurther information: Battles of the IsonzoAustro-Hungarian troops, Tyrol.Italy had been allied with the German and Austro-Hungarian Empires since 1882 as part of the Triple Alliance. However, the nation had its own designs on Austrian territory in Trentino, the Austrian Littoral, Fiume (Rijeka) and Dalmatia. Rome had a secret 1902 pact with France, effectively nullifying its part in the Triple Alliance.[109] At the start of hostilities, Italy refused to commit troops, arguing that the Triple Alliance was defensive and that Austria-Hungary was an aggressor. The Austro-Hungarian government began negotiations to secure Italian neutrality, offering the French colony of Tunisia in return. The Allies made a counter-offer in which Italy would receive the Southern Tyrol, Austrian Littoral and territory on the Dalmatian coast after the defeat of Austria-Hungary. This was formalised by the Treaty of London. Further encouraged by the Allied invasion of Turkey in April 1915, Italy joined the Triple Entente and declared war on Austria-Hungary on 23 May. Fifteen months later, Italy declared war on Germany.[110]Depiction of the Battle of Doberdò, fought in August 1916 between the Italian and the Austro-Hungarian armies
The Italians had numerical superiority but this advantage was lost, not only because of the difficult terrain in which the fighting took place, but also because of the strategies and tactics employed.[111] Field Marshal Luigi Cadorna, a staunch proponent of the frontal assault, had dreams of breaking into the Slovenian plateau, taking Ljubljana and threatening Vienna.
On the Trentino front, the Austro-Hungarians took advantage of the mountainous terrain, which favoured the defender. After an initial strategic retreat, the front remained largely unchanged, while Austrian Kaiserschützen and Standschützen engaged Italian Alpini in bitter hand-to-hand combat throughout the summer. The Austro-Hungarians counterattacked in the Altopiano of Asiago, towards Verona and Padua, in the spring of 1916 (Strafexpedition), but made little progress.[112]
Beginning in 1915, the Italians under Cadorna mounted eleven offensives on the Isonzo front along the Isonzo (Soča) River, northeast of Trieste. All eleven offensives were repelled by the Austro-Hungarians, who held the higher ground. In the summer of 1916, after the Battle of Doberdò, the Italians captured the town of Gorizia. After this minor victory, the front remained static for over a year, despite several Italian offensives, centred on the Banjšice and Karst Plateau east of Gorizia.
The Central Powers launched a crushing offensive on 26 October 1917, spearheaded by the Germans. They achieved a victory at Caporetto (Kobarid). The Italian Army was routed and retreated more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) to reorganise, stabilising the front at the Piave River. Since the Italian Army had suffered heavy losses in the Battle of Caporetto, the Italian Government called to arms the so-called '99 Boys (Ragazzi del '99): that is, all males born 1899 and prior, and so were 18 years old or older. In 1918, the Austro-Hungarians failed to break through in a series of battles on the Piave and were finally decisively defeated in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto in October of that year. On 1 November, the Italian Navy destroyed much of the Austro-Hungarian fleet stationed in Pula, preventing it from being handed over to the new State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. On 3 November, the Italians invaded Trieste from the sea. On the same day, the Armistice of Villa Giusti was signed. By mid-November 1918, the Italian military occupied the entire former Austrian Littoral and had seized control of the portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the London Pact.[113] By the end of hostilities in November 1918,[114] Admiral Enrico Millo declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia.[114] Austria-Hungary surrendered on 11 November 1918.[115][116]
Romanian participation
Main article: Romania during World War IMarshal Joffre inspecting Romanian troops, 1916Romania had been allied with the Central Powers since 1882. When the war began, however, it declared its neutrality, arguing that because Austria-Hungary had itself declared war on Serbia, Romania was under no obligation to join the war. When the Entente Powers promised Romania Transylvania and Banat, large territories of eastern Hungary, in exchange for Romania's declaring war on the Central Powers, the Romanian government renounced its neutrality. On 27 August 1916, the Romanian Army launched an attack against Austria-Hungary, with limited Russian support. The Romanian offensive was initially successful, against the Austro-Hungarian troops in Transylvania, but a counterattack by the forces of the Central Powers drove them back.[117] As a result of the Battle of Bucharest, the Central Powers occupied Bucharest on 6 December 1916. Fighting in Moldova continued in 1917, resulting in a costly stalemate for the Central Powers.[118][119] Russian withdrawal from the war in late 1917 as a result of the October Revolution meant that Romania was forced to sign an armistice with the Central Powers on 9 December 1917.Romanian troops during the Battle of Mărăşeşti, 1917
In January 1918, Romanian forces established control over Bessarabia as the Russian Army abandoned the province. Although a treaty was signed by the Romanian and the Bolshevik Russian governments following talks from 5–9 March 1918 on the withdrawal of Romanian forces from Bessarabia within two months, on 27 March 1918 Romania attached Bessarabia to its territory, formally based on a resolution passed by the local assembly of that territory on its unification with Romania.[120]
Romania officially made peace with the Central Powers by signing the Treaty of Bucharest on 7 May 1918. Under that treaty, Romania was obliged to end the war with the Central Powers and make small territorial concessions to Austria-Hungary, ceding control of some passes in the Carpathian Mountains, and to grant oil concessions to Germany. In exchange, the Central Powers recognised the sovereignty of Romania over Bessarabia. The treaty was renounced in October 1918 by the Alexandru Marghiloman government, and Romania nominally re-entered the war on 10 November 1918. The next day, the Treaty of Bucharest was nullified by the terms of the Armistice of Compiègne.[121][122] Total Romanian deaths from 1914 to 1918, military and civilian, within contemporary borders, were estimated at 748,000.[123]
Eastern Front
Main article: Eastern Front (World War I)Heir Presumptive Karl visiting Fortress of Przemyśl after the first siege. The Russian Siege of Przemyśl was the longest siege of the war.Initial actions
While the Western Front had reached stalemate, the war continued in East Europe.[124] Initial Russian plans called for simultaneous invasions of Austrian Galicia and East Prussia. Although Russia's initial advance into Galicia was largely successful, it was driven back from East Prussia by Hindenburg and Ludendorff at the Battle of Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes in August and September 1914.[125][126] Russia's less developed industrial base and ineffective military leadership were instrumental in the events that unfolded. By the spring of 1915, the Russians had retreated to Galicia, and, in May, the Central Powers achieved a remarkable breakthrough on Poland's southern frontiers.[127] On 5 August, they captured Warsaw and forced the Russians to withdraw from Poland.
Russian Revolution
Main article: Russian RevolutionDespite Russia's success with the June 1916 Brusilov Offensive in eastern Galicia,[128] dissatisfaction with the Russian government's conduct of the war grew. The offensive's success was undermined by the reluctance of other generals to commit their forces to support the victory. Allied and Russian forces were revived only temporarily by Romania's entry into the war on 27 August. German forces came to the aid of embattled Austro-Hungarian units in Transylvania while a German-Bulgarian force attacked from the south, and Bucharest was retaken by the Central Powers on 6 December. Meanwhile, unrest grew in Russia, as the Tsar remained at the front. Empress Alexandra's increasingly incompetent rule drew protests and resulted in the murder of her favourite, Rasputin, at the end of 1916.American, British, and Japanese Troops parade through Vladivostok in armed support to the White Army
In March 1917, demonstrations in Petrograd culminated in the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II and the appointment of a weak Provisional Government, which shared power with the Petrograd Soviet socialists. This arrangement led to confusion and chaos both at the front and at home. The army became increasingly ineffective.[127]
Following the Tsar's abdication, Vladimir Lenin was ushered by train from Switzerland into Russia 16 April 1917. He was financed by Jacob Schiff.[129] Discontent and the weaknesses of the Provisional Government led to a rise in the popularity of the Bolshevik Party, led by Lenin, which demanded an immediate end to the war. The Revolution of November was followed in December by an armistice and negotiations with Germany. At first, the Bolsheviks refused the German terms, but when German troops began marching across Ukraine unopposed, the new government acceded to the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk on 3 March 1918. The treaty ceded vast territories, including Finland, the Baltic provinces, parts of Poland and Ukraine to the Central Powers.[130] Despite this enormous apparent German success, the manpower required for German occupation of former Russian territory may have contributed to the failure of the Spring Offensive and secured relatively little food or other materiel for the Central Powers war effort.
With the adoption of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, the Entente no longer existed. The Allied powers led a small-scale invasion of Russia, partly to stop Germany from exploiting Russian resources, and to a lesser extent, to support the "Whites" (as opposed to the "Reds") in the Russian Civil War.[131] Allied troops landed in Arkhangelsk and in Vladivostok as part of the North Russia Intervention.
Czechoslovak Legion
Czechoslovak Legion, Vladivostok, 1918.Main article: Czechoslovak LegionThe Czechoslovak Legion fought with the Entente; their goal was to win support for the independence of Czechoslovakia. The Legion in Russia was established in September 1914, in December 1917 in France (including volunteers from America) and in April 1918 in Italy. Czechoslovak Legion troops defeated the Austro-Hungarian army at the Ukrainian village of Zborov, in July 1917. After this success, the number of Czechoslovak legionaries increased, as well as Czechoslovak military power. In the Battle of Bakhmach, the Legion defeated the Germans and forced them to make a truce.
In Russia, they were heavily involved in the Russian Civil War, siding with the Whites against the Bolsheviks, at times controlling most of the Trans-Siberian railway and conquering all the major cities of Siberia. The presence of the Czechoslovak Legion near Yekaterinburg appears to have been one of the motivations for the Bolshevik execution of the Tsar and his family in July 1918. Legionaries arrived less than a week afterwards and captured the city. Because Russia's European ports were not safe, the corps was evacuated by a long detour via the port of Vladivostok. The last transport was the American ship Heffron in September 1920.
Central Powers peace overtures
In December 1916, after ten brutal months of the Battle of Verdun and a successful offensive against Romania, the Germans attempted to negotiate a peace with the Allies. Soon after, the US president, Woodrow Wilson, attempted to intervene as a peacemaker, asking in a note for both sides to state their demands. Lloyd George's War Cabinet considered the German offer to be a ploy to create divisions amongst the Allies. After initial outrage and much deliberation, they took Wilson's note as a separate effort, signalling that the United States was on the verge of entering the war against Germany following the "submarine outrages". While the Allies debated a response to Wilson's offer, the Germans chose to rebuff it in favour of "a direct exchange of views". Learning of the German response, the Allied governments were free to make clear demands in their response of 14 January. They sought restoration of damages, the evacuation of occupied territories, reparations for France, Russia and Romania, and a recognition of the principle of nationalities. This included the liberation of Italians, Slavs, Romanians, Czecho-Slovaks, and the creation of a "free and united Poland". On the question of security, the Allies sought guarantees that would prevent or limit future wars, complete with sanctions, as a condition of any peace settlement.[132] The negotiations failed and the Entente powers rejected the German offer, because Germany did not state any specific proposals. The Entente powers stated to Wilson that they would not start peace negotiations until the Central powers evacuated all occupied Allied territories and provided indemnities for all damage which had been done.[133]"They shall not pass", a phrase typically associated with the defense of Verdun.
1917–1918
Developments in 1917
French Army lookout at his observation post, Haut-Rhin, France, 1917.Events of 1917 proved decisive in ending the war, although their effects were not fully felt until 1918.German film crew recording the action.
The British naval blockade began to have a serious impact on Germany. In response, in February 1917, the German General Staff convinced Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg to declare unrestricted submarine warfare, with the goal of starving Britain out of the war. German planners estimated that unrestricted submarine warfare would cost Britain a monthly shipping loss of 600,000 tons. The General Staff acknowledged that the policy would almost certainly bring the United States into the conflict, but calculated that British shipping losses would be so high that they would be forced to sue for peace after 5 to 6 months, before American intervention could make an impact. In reality, tonnage sunk rose above 500,000 tons per month from February to July. It peaked at 860,000 tons in April. After July, the newly re-introduced convoy system became effective in reducing the U-boat threat. Britain was safe from starvation, while German industrial output fell and the United States joined the war far earlier than Germany had anticipated.
On 3 May 1917, during the Nivelle Offensive, the French 2nd Colonial Division, veterans of the Battle of Verdun, refused orders, arriving drunk and without their weapons. Their officers lacked the means to punish an entire division, and harsh measures were not immediately implemented. The French Army Mutinies eventually spread to a further 54 French divisions and saw 20,000 men desert. However, appeals to patriotism and duty, as well as mass arrests and trials, encouraged the soldiers to return to defend their trenches, although the French soldiers refused to participate in further offensive action.[134] Robert Nivelle was removed from command by 15 May, replaced by General Philippe Pétain, who suspended bloody large-scale attacks.
The victory of the Central Powers at the Battle of Caporetto led the Allies to convene the Rapallo Conference at which they formed the Supreme War Council to coordinate planning. Previously, British and French armies had operated under separate commands.
In December, the Central Powers signed an armistice with Russia, thus freeing large numbers of German troops for use in the west. With German reinforcements and new American troops pouring in, the outcome was to be decided on the Western Front. The Central Powers knew that they could not win a protracted war, but they held high hopes for success based on a final quick offensive. Furthermore, both sides became increasingly fearful of social unrest and revolution in Europe. Thus, both sides urgently sought a decisive victory.[135]
In 1917, Emperor Charles I of Austria secretly attempted separate peace negotiations with Clemenceau, through his wife's brother Sixtus in Belgium as an intermediary, without the knowledge of Germany. Italy opposed the proposals. When the negotiations failed, his attempt was revealed to Germany, resulting in a diplomatic catastrophe.[136][137]
Ottoman Empire conflict, 1917–1918
Main article: Sinai and Palestine Campaign10.5 cm Feldhaubitze 98/09 and Ottoman artillerymen at Hareira in 1917 before the Southern Palestine offensive.Ottoman troops during Mesopotamian campaign.British artillery battery on Mount Scopus in the Battle of Jerusalem, 1917.In March and April 1917, at the First and Second Battles of Gaza, German and Ottoman forces stopped the advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, which had begun in August 1916 at the Battle of Romani.[138][139] At the end of October, the Sinai and Palestine Campaign resumed, when General Edmund Allenby's XXth Corps, XXI Corps and Desert Mounted Corps won the Battle of Beersheba.[140] Two Ottoman armies were defeated a few weeks later at the Battle of Mughar Ridge and, early in December, Jerusalem was captured following another Ottoman defeat at the Battle of Jerusalem (1917).[141][142][143] About this time, Friedrich Freiherr Kress von Kressenstein was relieved of his duties as the Eighth Army's commander, replaced by Djevad Pasha, and a few months later the commander of the Ottoman Army in Palestine, Erich von Falkenhayn, was replaced by Otto Liman von Sanders.[144][145]British troops on the march during Mesopotamian campaign, 1917
In early 1918, the front line was extended and the Jordan Valley was occupied, following the First Transjordan and the Second Transjordan attack by British Empire forces in March and April 1918.[146] In March, most of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force's British infantry and Yeomanry cavalry were sent to the Western Front as a consequence of the Spring Offensive. They were replaced by Indian Army units. During several months of reorganisation and training of the summer, a number of attacks were carried out on sections of the Ottoman front line. These pushed the front line north to more advantageous positions for the Entente in preparation for an attack and to acclimatise the newly arrived Indian Army infantry. It was not until the middle of September that the integrated force was ready for large-scale operations.
The reorganised Egyptian Expeditionary Force, with an additional mounted division, broke Ottoman forces at the Battle of Megiddo in September 1918. In two days the British and Indian infantry, supported by a creeping barrage, broke the Ottoman front line and captured the headquarters of the Eighth Army (Ottoman Empire) at Tulkarm, the continuous trench lines at Tabsor, Arara and the Seventh Army (Ottoman Empire) headquarters at Nablus. The Desert Mounted Corps rode through the break in the front line created by the infantry and, during virtually continuous operations by Australian Light Horse, British mounted Yeomanry, Indian Lancers and New Zealand Mounted Rifle brigades in the Jezreel Valley, they captured Nazareth, Afulah and Beisan, Jenin, along with Haifa on the Mediterranean coast and Daraa east of the Jordan River on the Hejaz railway. Samakh and Tiberias on the Sea of Galilee, were captured on the way northwards to Damascus. Meanwhile, Chaytor's Force of Australian light horse, New Zealand mounted rifles, Indian, British West Indies and Jewish infantry captured the crossings of the Jordan River, Es Salt, Amman and at Ziza most of the Fourth Army (Ottoman Empire). The Armistice of Mudros, signed at the end of October, ended hostilities with the Ottoman Empire when fighting was continuing north of Aleppo.
Entry of the United States
Main article: American entry into World War IAt the outbreak of the war, the United States pursued a policy of non-intervention, avoiding conflict while trying to broker a peace. When the German U-boat U-20 sank the British liner RMS Lusitania on 7 May 1915 with 128 Americans among the dead, President Woodrow Wilson insisted that "America is too proud to fight" but demanded an end to attacks on passenger ships. Germany complied. Wilson unsuccessfully tried to mediate a settlement. However, he also repeatedly warned that the United States would not tolerate unrestricted submarine warfare, in violation of international law. Former president Theodore Roosevelt denounced German acts as "piracy".[147] Wilson was narrowly reelected in 1916 as his supporters emphasized "he kept us out of war".President Wilson before Congress, announcing the break in official relations with Germany on 3 February 1917
In January 1917, Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare, realizing it would mean American entry. The German Foreign Minister, in the Zimmermann Telegram, invited Mexico to join the war as Germany's ally against the United States. In return, the Germans would finance Mexico's war and help it recover the territories of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona.[148] The United Kingdom intercepted the message and presented it to the US embassy in the UK. From there it made its way to President Wilson who released the Zimmermann note to the public, and Americans saw it as casus belli. Wilson called on antiwar elements to end all wars, by winning this one and eliminating militarism from the globe. He argued that the war was so important that the US had to have a voice in the peace conference.[149] After the sinking of seven US merchant ships by submarines and the publication of the Zimmermann telegram, Wilson called for war on Germany,[150] which the US Congress declared on 6 April 1917.
The United States was never formally a member of the Allies but became a self-styled "Associated Power". The United States had a small army, but, after the passage of the Selective Service Act, it drafted 2.8 million men,[151] and, by summer 1918, was sending 10,000 fresh soldiers to France every day. In 1917, the US Congress gave US citizenship to Puerto Ricans when they were drafted to participate in World War I, as part of the Jones Act. If Germany believed it would be many more months before American soldiers would arrive and that their arrival could be stopped by U-boats, it had miscalculated.[152]
The United States Navy sent a battleship group to Scapa Flow to join with the British Grand Fleet, destroyers to Queenstown, Ireland, and submarines to help guard convoys. Several regiments of US Marines were also dispatched to France. The British and French wanted American units used to reinforce their troops already on the battle lines and not waste scarce shipping on bringing over supplies. General John J. Pershing, American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) commander, refused to break up American units to be used as filler material. As an exception, he did allow African-American combat regiments to be used in French divisions. The Harlem Hellfighters fought as part of the French 16th Division, and earned a unit Croix de Guerre for their actions at Château-Thierry, Belleau Wood, and Sechault.[153] AEF doctrine called for the use of frontal assaults, which had long since been discarded by British Empire and French commanders due to the large loss of life that resulted.[154]
German Spring Offensive of 1918
Main article: Spring OffensiveBritish 55th Division soldiers, blinded by tear gas during the Battle of Estaires, 10 April 1918Ludendorff drew up plans (codenamed Operation Michael) for the 1918 offensive on the Western Front. The Spring Offensive sought to divide the British and French forces with a series of feints and advances. The German leadership hoped to end the war before significant US forces arrived. The operation commenced on 21 March 1918, with an attack on British forces near Saint-Quentin. German forces achieved an unprecedented advance of 60 kilometres (37 mi).[155]French soldiers under General Gouraud, with machine guns amongst the ruins of a cathedral near the Marne, 1918.
British and French trenches were penetrated using novel infiltration tactics, also named Hutier tactics, after General Oskar von Hutier, by specially trained units called stormtroopers. Previously, attacks had been characterised by long artillery bombardments and massed assaults. However, in the Spring Offensive of 1918, Ludendorff used artillery only briefly and infiltrated small groups of infantry at weak points. They attacked command and logistics areas and bypassed points of serious resistance. More heavily armed infantry then destroyed these isolated positions. This German success relied greatly on the element of surprise.[156]
The front moved to within 120 kilometres (75 mi) of Paris. Three heavy Krupp railway guns fired 183 shells on the capital, causing many Parisians to flee. The initial offensive was so successful that Kaiser Wilhelm II declared 24 March a national holiday. Many Germans thought victory was near. After heavy fighting, however, the offensive was halted. Lacking tanks or motorised artillery, the Germans were unable to consolidate their gains. The problems of re-supply were also exacerbated by increasing distances that now stretched over terrain that was shell-torn and often impassable to traffic.[157]
General Foch pressed to use the arriving American troops as individual replacements, whereas Pershing sought to field American units as an independent force. These units were assigned to the depleted French and British Empire commands on 28 March. A Supreme War Council of Allied forces was created at the Doullens Conference on 5 November 1917. General Foch was appointed as supreme commander of the Allied forces. Haig, Petain, and Pershing retained tactical control of their respective armies; Foch assumed a coordinating rather than a directing role, and the British, French, and US commands operated largely independently.[158]
Following Operation Michael, Germany launched Operation Georgette against the northern English Channel ports. The Allies halted the drive after limited territorial gains by Germany. The German Army to the south then conducted Operations Blücher and Yorck, pushing broadly towards Paris. Germany launched Operation Marne (Second Battle of the Marne) 15 July, in an attempt to encircle Reims. The resulting counterattack, which started the Hundred Days Offensive, marked the first successful Allied offensive of the war.
By 20 July, the Germans had retreated across the Marne to their starting lines,[159] having achieved little, and the German Army never regained the initiative. German casualties between March and April 1918 were 270,000, including many highly trained storm troopers.
Meanwhile, Germany was falling apart at home. Anti-war marches became frequent and morale in the army fell. Industrial output was half the 1913 levels.
New states under war zone
In the late spring of 1918, three new states were formed in the South Caucasus: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic, and the Democratic Republic of Georgia, which declared their independence from the Russian Empire. Two other minor entities were established, the Centrocaspian Dictatorship and South West Caucasian Republic (the former was liquidated by Azerbaijan in the autumn of 1918 and the latter by a joint Armenian-British task force in early 1919). With the withdrawal of the Russian armies from the Caucasus front in the winter of 1917–18, the three major republics braced for an imminent Ottoman advance, which commenced in the early months of 1918. Solidarity was briefly maintained when the Transcaucasian Federative Republic was created in the spring of 1918, but this collapsed in May, when the Georgians asked for and received protection from Germany and the Azerbaijanis concluded a treaty with the Ottoman Empire that was more akin to a military alliance. Armenia was left to fend for itself and struggled for five months against the threat of a full-fledged occupation by the Ottoman Turks before defeating them at the Battle of Sardarabad.[160]
Allied victory: summer 1918 onwards
Allies increased their front-line rifle strength while German strength fell in half in 1918[161]Hundred Days Offensive
Main articles: Hundred Days Offensive and Weimar RepublicThe Allied counteroffensive, known as the Hundred Days Offensive, began on 8 August 1918, with the Battle of Amiens. The battle involved over 400 tanks and 120,000 British, Dominion, and French troops, and by the end of its first day a gap 24 kilometres (15 mi) long had been created in the German lines. The defenders displayed a marked collapse in morale, causing Ludendorff to refer to this day as the "Black Day of the German army".[162][163][better source needed] After an advance as far as 23 kilometres (14 mi), German resistance stiffened, and the battle was concluded on 12 August.Aerial view of ruins of Vaux-devant-Damloup, France, 1918.
Rather than continuing the Amiens battle past the point of initial success, as had been done so many times in the past, the Allies shifted their attention elsewhere. Allied leaders had now realised that to continue an attack after resistance had hardened was a waste of lives, and it was better to turn a line than to try to roll over it. They began to undertake attacks in quick order to take advantage of successful advances on the flanks, then broke them off when each attack lost its initial impetus.[164]
British and Dominion forces launched the next phase of the campaign with the Battle of Albert on 21 August.[165] The assault was widened by French[166] and then further British forces in the following days. During the last week of August the Allied pressure along a 110-kilometre (68 mi) front against the enemy was heavy and unrelenting. From German accounts, "Each day was spent in bloody fighting against an ever and again on-storming enemy, and nights passed without sleep in retirements to new lines."[164]Canadian Scottish, advancing during the Battle of the Canal du Nord, 1918
Faced with these advances, on 2 September the German Supreme Army Command issued orders to withdraw to the Hindenburg Line in the south. This ceded without a fight the salient seized the previous April.[167] According to Ludendorff "We had to admit the necessity ... to withdraw the entire front from the Scarpe to the Vesle.[168]
September saw the Allies advance to the Hindenburg Line in the north and centre. The Germans continued to fight strong rear-guard actions and launched numerous counterattacks on lost positions, but only a few succeeded, and those only temporarily. Contested towns, villages, heights, and trenches in the screening positions and outposts of the Hindenburg Line continued to fall to the Allies, with the BEF alone taking 30,441 prisoners in the last week of September. On 24 September an assault by both the British and French came within 3 kilometres (2 mi) of St. Quentin.[166] The Germans had now retreated to positions along or behind the Hindenburg Line.
In nearly four weeks of fighting beginning 8 August, over 100,000 German prisoners were taken. As of "The Black Day of the German Army", the German High Command realised that the war was lost and made attempts to reach a satisfactory end. The day after that battle, Ludendorff said: "We cannot win the war any more, but we must not lose it either." On 11 August he offered his resignation to the Kaiser, who refused it, replying, "I see that we must strike a balance. We have nearly reached the limit of our powers of resistance. The war must be ended." On 13 August, at Spa, Hindenburg, Ludendorff, the Chancellor, and Foreign Minister Hintz agreed that the war could not be ended militarily and, on the following day, the German Crown Council decided that victory in the field was now most improbable. Austria and Hungary warned that they could only continue the war until December, and Ludendorff recommended immediate peace negotiations. Prince Rupprecht warned Prince Max of Baden: "Our military situation has deteriorated so rapidly that I no longer believe we can hold out over the winter; it is even possible that a catastrophe will come earlier." On 10 September Hindenburg urged peace moves to Emperor Charles of Austria, and Germany appealed to the Netherlands for mediation. On 14 September Austria sent a note to all belligerents and neutrals suggesting a meeting for peace talks on neutral soil, and on 15 September Germany made a peace offer to Belgium. Both peace offers were rejected, and on 24 September Supreme Army Command informed the leaders in Berlin that armistice talks were inevitable.[166]An American major, piloting an observation balloon near the front, 1918
The final assault on the Hindenburg Line began with the Meuse-Argonne Offensive, launched by French and American troops on 26 September. The following week, cooperating French and American units broke through in Champagne at the Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge, forcing the Germans off the commanding heights, and closing towards the Belgian frontier.[169] On 8 October the line was pierced again by British and Dominion troops at the Battle of Cambrai.[170] The German army had to shorten its front and use the Dutch frontier as an anchor to fight rear-guard actions as it fell back towards Germany.
When Bulgaria signed a separate armistice on 29 September, Ludendorff, having been under great stress for months, suffered something similar to a breakdown. It was evident that Germany could no longer mount a successful defence.[171][172]
News of Germany's impending military defeat spread throughout the German armed forces. The threat of mutiny was rife. Admiral Reinhard Scheer and Ludendorff decided to launch a last attempt to restore the "valour" of the German Navy. Knowing the government of Prince Maximilian of Baden would veto any such action, Ludendorff decided not to inform him. Nonetheless, word of the impending assault reached sailors at Kiel. Many, refusing to be part of a naval offensive, which they believed to be suicidal, rebelled and were arrested. Ludendorff took the blame; the Kaiser dismissed him on 26 October. The collapse of the Balkans meant that Germany was about to lose its main supplies of oil and food. Its reserves had been used up, even as US troops kept arriving at the rate of 10,000 per day.[173] The Americans supplied more than 80% of Allied oil during the war, and there was no shortage.[174]Men of US 64th Regiment, 7th Infantry Division, celebrate the news of the Armistice, 11 November 1918.
With the military faltering and with widespread loss of confidence in the Kaiser, Germany moved towards surrender. Prince Maximilian of Baden took charge of a new government as Chancellor of Germany to negotiate with the Allies. Negotiations with President Wilson began immediately, in the hope that he would offer better terms than the British and French. Wilson demanded a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary control over the German military.[175] There was no resistance when the Social Democrat Philipp Scheidemann on 9 November declared Germany to be a republic. The Kaiser, kings and other hereditary rulers all were removed from power and Wilhelm fled to exile in the Netherlands. Imperial Germany was dead; a new Germany had been born as the Weimar Republic.[176]
Armistices and capitulations
Main article: Armistice of 11 November 1918The New York Times of 11 November 1918The collapse of the Central Powers came swiftly. Bulgaria was the first to sign an armistice, on 29 September 1918 at Saloniki.[178] On 30 October, the Ottoman Empire capitulated, signing the Armistice of Mudros.[178]Ferdinand Foch, second from right, pictured outside the carriage in Compiègne after agreeing to the armistice that ended the war there. The carriage was later chosen by Nazi Germany as the symbolic setting of Pétain's June 1940 armistice.[177]
On 24 October, the Italians began a push that rapidly recovered territory lost after the Battle of Caporetto. This culminated in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, which marked the end of the Austro-Hungarian Army as an effective fighting force. The offensive also triggered the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. During the last week of October, declarations of independence were made in Budapest, Prague, and Zagreb. On 29 October, the imperial authorities asked Italy for an armistice. But the Italians continued advancing, reaching Trento, Udine, and Trieste. On 3 November, Austria-Hungary sent a flag of truce to ask for an armistice (Armistice of Villa Giusti). The terms, arranged by telegraph with the Allied Authorities in Paris, were communicated to the Austrian commander and accepted. The Armistice with Austria was signed in the Villa Giusti, near Padua, on 3 November. Austria and Hungary signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the Habsburg Monarchy.
On 11 November, at 5:00 am, an armistice with Germany was signed in a railroad carriage at Compiègne. At 11 am on 11 November 1918—"the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month"—a ceasefire came into effect. During the six hours between the signing of the armistice and its taking effect, opposing armies on the Western Front began to withdraw from their positions, but fighting continued along many areas of the front, as commanders wanted to capture territory before the war ended.
The occupation of the Rhineland took place following the Armistice. The occupying armies consisted of American, Belgian, British and French forces.
In November 1918, the Allies had ample supplies of men and materiel to invade Germany. Yet at the time of the armistice, no Allied force had crossed the German frontier; the Western Front was still some 720 kilometres (450 mi) from Berlin; and the Kaiser's armies had retreated from the battlefield in good order. These factors enabled Hindenburg and other senior German leaders to spread the story that their armies had not really been defeated. This resulted in the stab-in-the-back legend,[179][180] which attributed Germany's defeat not to its inability to continue fighting (even though up to a million soldiers were suffering from the 1918 flu pandemic and unfit to fight), but to the public's failure to respond to its "patriotic calling" and the supposed intentional sabotage of the war effort, particularly by Jews, Socialists, and Bolsheviks.
The Allies had much more potential wealth they could spend on the war. One estimate (using 1913 US dollars) is that the Allies spent $58 billion on the war and the Central Powers only $25 billion. Among the Allies, the UK spent $21 billion and the US $17 billion; among the Central Powers Germany spent $20 billion.[181]
Aftermath
Main article: Aftermath of World War IIn the aftermath of the war, four empires disappeared: the German, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, and Russian. Numerous nations regained their former independence, and new ones were created. Four dynasties, together with their ancillary aristocracies, all fell as a result of the war: the Romanovs, the Hohenzollerns, the Habsburgs, and the Ottomans. Belgium and Serbia were badly damaged, as was France, with 1.4 million soldiers dead,[182] not counting other casualties. Germany and Russia were similarly affected.[183]The French military cemetery at the Douaumont ossuary, which contains the remains of more than 130,000 unknown soldiers
Formal end of the war
A formal state of war between the two sides persisted for another seven months, until the signing of the Treaty of Versailles with Germany on 28 June 1919. The United States Senate did not ratify the treaty despite public support for it,[184][185] and did not formally end its involvement in the war until the Knox–Porter Resolution was signed on 2 July 1921 by President Warren G. Harding.[186] For the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the state of war ceased under the provisions of the Termination of the Present War (Definition) Act 1918 with respect to:
Some war memorials date the end of the war as being when the Versailles Treaty was signed in 1919, which was when many of the troops serving abroad finally returned to their home countries; by contrast, most commemorations of the war's end concentrate on the armistice of 11 November 1918. Legally, the formal peace treaties were not complete until the last, the Treaty of Lausanne, was signed. Under its terms, the Allied forces left Constantinople on 23 August 1923.
Peace treaties and national boundaries
Greek prime minister Eleftherios Venizelos signing the Treaty of SèvresAfter the war, the Paris Peace Conference imposed a series of peace treaties on the Central Powers officially ending the war. The 1919 Treaty of Versailles dealt with Germany and, building on Wilson's 14th point, brought into being the League of Nations on 28 June 1919.[192][193]The Signing of Peace in the Hall of Mirrors, Versailles, 28 June 1919
The Central Powers had to acknowledge responsibility for "all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by" their aggression. In the Treaty of Versailles, this statement was Article 231. This article became known as War Guilt clause as the majority of Germans felt humiliated and resentful.[194] Overall the Germans felt they had been unjustly dealt by what they called the "diktat of Versailles". Schulze said the Treaty placed Germany "under legal sanctions, deprived of military power, economically ruined, and politically humiliated."[195] Belgian historian Laurence Van Ypersele emphasizes the central role played by memory of the war and the Versailles Treaty in German politics in the 1920s and 1930s:
Active denial of war guilt in Germany and German resentment at both reparations and continued Allied occupation of the Rhineland made widespread revision of the meaning and memory of the war problematic. The legend of the "stab in the back" and the wish to revise the "Versailles diktat", and the belief in an international threat aimed at the elimination of the German nation persisted at the heart of German politics. Even a man of peace such as Stresemann publicly rejected German guilt. As for the Nazis, they waved the banners of domestic treason and international conspiracy in an attempt to galvanize the German nation into a spirit of revenge. Like a Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany sought to redirect the memory of the war to the benefit of its own policies.[196]
Meanwhile, new nations liberated from German rule viewed the treaty as recognition of wrongs committed against small nations by much larger aggressive neighbors.[197] The Peace Conference required all the defeated powers to pay reparations for all the damage done to civilians. However, owing to economic difficulties and Germany being the only defeated power with an intact economy, the burden fell largely on Germany.
Austria-Hungary was partitioned into several successor states, including Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia, largely but not entirely along ethnic lines. Transylvania was shifted from Hungary to Greater Romania. The details were contained in the Treaty of Saint-Germain and the Treaty of Trianon. As a result of the Treaty of Trianon, 3.3 million Hungarians came under foreign rule. Although the Hungarians made up 54% of the population of the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, only 32% of its territory was left to Hungary. Between 1920 and 1924, 354,000 Hungarians fled former Hungarian territories attached to Romania, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia.[198]
The Russian Empire, which had withdrawn from the war in 1917 after the October Revolution, lost much of its western frontier as the newly independent nations of Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland were carved from it. Romania took control of Bessarabia in April 1918.[199]
The Ottoman Empire disintegrated, with much of its Levant territory awarded to various Allied powers as protectorates. The Turkish core in Anatolia was reorganised as the Republic of Turkey. The Ottoman Empire was to be partitioned by the Treaty of Sèvres of 1920. This treaty was never ratified by the Sultan and was rejected by the Turkish National Movement, leading to the victorious Turkish War of Independence and the much less stringent 1923 Treaty of Lausanne.
National identities
Further information: Sykes–Picot AgreementPoland reemerged as an independent country, after more than a century. The Kingdom of Serbia and its dynasty, as a "minor Entente nation" and the country with the most casualties per capita,[200][201][202] became the backbone of a new multinational state, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, later renamed Yugoslavia. Czechoslovakia, combining the Kingdom of Bohemia with parts of the Kingdom of Hungary, became a new nation. Russia became the Soviet Union and lost Finland, Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia, which became independent countries. The Ottoman Empire was soon replaced by Turkey and several other countries in the Middle East.Map of territorial changes in Europe after World War I (as of 1923)
In the British Empire, the war unleashed new forms of nationalism. In Australia and New Zealand the Battle of Gallipoli became known as those nations' "Baptism of Fire". It was the first major war in which the newly established countries fought, and it was one of the first times that Australian troops fought as Australians, not just subjects of the British Crown. Anzac Day, commemorating the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps, celebrates this defining moment.[203][204]
After the Battle of Vimy Ridge, where the Canadian divisions fought together for the first time as a single corps, Canadians began to refer to theirs as a nation "forged from fire".[205] Having succeeded on the same battleground where the "mother countries" had previously faltered, they were for the first time respected internationally for their own accomplishments. Canada entered the war as a Dominion of the British Empire and remained so, although it emerged with a greater measure of independence.[206][207] When Britain declared war in 1914, the dominions were automatically at war; at the conclusion, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa were individual signatories of the Treaty of Versailles.[208]
The establishment of the modern state of Israel and the roots of the continuing Israeli–Palestinian conflict are partially found in the unstable power dynamics of the Middle East that resulted from World War I.[209] Before the end of the war, the Ottoman Empire had maintained a modest level of peace and stability throughout the Middle East.[210] With the fall of the Ottoman government, power vacuums developed and conflicting claims to land and nationhood began to emerge.[211] The political boundaries drawn by the victors of World War I were quickly imposed, sometimes after only cursory consultation with the local population. These continue to be problematic in the 21st-century struggles for national identity.[212][213] While the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire at the end of World War I was pivotal in contributing to the modern political situation of the Middle East, including the Arab-Israeli conflict,[214][215][216] the end of Ottoman rule also spawned lesser known disputes over water and other natural resources.[217]
Health effects
Transporting Ottoman wounded at SirkeciThe war had profound consequences in the health of soldiers. Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilized from 1914 to 1918, 8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured. Germany lost 15.1% of its active male population, Austria-Hungary lost 17.1%, and France lost 10.5%.[218] In Germany, civilian deaths were 474,000 higher than in peacetime, due in large part to food shortages and malnutrition that weakened resistance to disease.[219] By the end of the war, starvation caused by famine had killed approximately 100,000 people in Lebanon.[220] Between 5 and 10 million people died in the Russian famine of 1921.[221] By 1922, there were between 4.5 million and 7 million homeless children in Russia as a result of nearly a decade of devastation from World War I, the Russian Civil War, and the subsequent famine of 1920–1922.[222] Numerous anti-Soviet Russians fled the country after the Revolution; by the 1930s, the northern Chinese city of Harbin had 100,000 Russians.[223] Thousands more emigrated to France, England, and the United States.Emergency military hospital during the Spanish flu pandemic, which killed about 675,000 people in the United States alone. Camp Funston, Kansas, 1918.
In Australia, the effects of the war on the economy were no less severe. The Australian prime minister, Billy Hughes, wrote to the British prime minister, Lloyd George, "You have assured us that you cannot get better terms. I much regret it, and hope even now that some way may be found of securing agreement for demanding reparation commensurate with the tremendous sacrifices made by the British Empire and her Allies." Australia received ₤5,571,720 war reparations, but the direct cost of the war to Australia had been ₤376,993,052, and, by the mid-1930s, repatriation pensions, war gratuities, interest and sinking fund charges were ₤831,280,947.[224] Of about 416,000 Australians who served, about 60,000 were killed and another 152,000 were wounded.[225]
Diseases flourished in the chaotic wartime conditions. In 1914 alone, louse-borne epidemic typhus killed 200,000 in Serbia.[226] From 1918 to 1922, Russia had about 25 million infections and 3 million deaths from epidemic typhus.[227] In 1923, 13 million Russians contracted malaria, a sharp increase from the pre-war years.[228] In addition, a major influenza epidemic spread around the world. Overall, the 1918 flu pandemic killed at least 50 million people.[229][230]
Lobbying by Chaim Weizmann and fear that American Jews would encourage the United States to support Germany culminated in the British government's Balfour Declaration of 1917, endorsing creation of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.[231] A total of more than 1,172,000 Jewish soldiers served in the Allied and Central Power forces in World War I, including 275,000 in Austria-Hungary and 450,000 in Tsarist Russia.[232]
The social disruption and widespread violence of the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the ensuing Russian Civil War sparked more than 2,000 pogroms in the former Russian Empire, mostly in Ukraine.[233] An estimated 60,000–200,000 civilian Jews were killed in the atrocities.[234]
In the aftermath of World War I, Greece fought against Turkish nationalists led by Mustafa Kemal, a war which eventually resulted in a massive population exchange between the two countries under the Treaty of Lausanne.[235] According to various sources,[236] several hundred thousand Greeks died during this period, which was tied in with the Greek Genocide.[237]
Technology
See also: Technology during World War I and Weapons of World War IGround warfare
See also: Tanks in World War ITanks on parade in London at the end of World War IWorld War I began as a clash of 20th-century technology and 19th-century tactics, with the inevitably large ensuing casualties. By the end of 1917, however, the major armies, now numbering millions of men, had modernised and were making use of telephone, wireless communication,[238] armoured cars, tanks,[239] and aircraft. Infantry formations were reorganised, so that 100-man companies were no longer the main unit of manoeuvre; instead, squads of 10 or so men, under the command of a junior NCO, were favoured.A Russian armoured car, 1919
Artillery also underwent a revolution. In 1914, cannons were positioned in the front line and fired directly at their targets. By 1917, indirect fire with guns (as well as mortars and even machine guns) was commonplace, using new techniques for spotting and ranging, notably aircraft and the often overlooked field telephone.[240] Counter-battery missions became commonplace, also, and sound detection was used to locate enemy batteries.
Germany was far ahead of the Allies in utilising heavy indirect fire. The German Army employed 150 mm (6 in) and 210 mm (8 in) howitzers in 1914, when typical French and British guns were only 75 mm (3 in) and 105 mm (4 in). The British had a 6-inch (152 mm) howitzer, but it was so heavy it had to be hauled to the field in pieces and assembled. The Germans also fielded Austrian 305 mm (12 in) and 420 mm (17 in) guns and, even at the beginning of the war, had inventories of various calibers of Minenwerfer, which were ideally suited for trench warfare.[241][242]
Much of the combat involved trench warfare, in which hundreds often died for each metre gained. Many of the deadliest battles in history occurred during World War I. Such battles include Ypres, the Marne, Cambrai, the Somme, Verdun, and Gallipoli. The Germans employed the Haber process of nitrogen fixation to provide their forces with a constant supply of gunpowder despite the British naval blockade.[243] Artillery was responsible for the largest number of casualties[244] and consumed vast quantities of explosives. The large number of head wounds caused by exploding shells and fragmentation forced the combatant nations to develop the modern steel helmet, led by the French, who introduced the Adrian helmet in 1915. It was quickly followed by the Brodie helmet, worn by British Imperial and US troops, and in 1916 by the distinctive German Stahlhelm, a design, with improvements, still in use today.
Gas! GAS! Quick, boys! – An ecstasy of fumbling,
Fitting the clumsy helmets just in time;
But someone still was yelling out and stumbling,
And flound'ring like a man in fire or lime ...
Dim, through the misty panes and thick green light,
As under a green sea, I saw him drowning.
The widespread use of chemical warfare was a distinguishing feature of the conflict. Gases used included chlorine, mustard gas and phosgene. Few war casualties were caused by gas,[246] as effective countermeasures to gas attacks were quickly created, such as gas masks. The use of chemical warfare and small-scale strategic bombing were both outlawed by the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907, and both proved to be of limited effectiveness,[247] though they captured the public imagination.[248]A Canadian soldier with mustard gas burns, ca. 1917–1918
The most powerful land-based weapons were railway guns, weighing dozens of tons apiece.[249] The German ones were nicknamed Big Berthas, even though the namesake was not a railway gun. Germany developed the Paris Gun, able to bombard Paris from over 100 kilometres (62 mi), though shells were relatively light at 94 kilograms (210 lb).
Trenches, machine guns, air reconnaissance, barbed wire, and modern artillery with fragmentation shells helped bring the battle lines of World War I to a stalemate. The British and the French sought a solution with the creation of the tank and mechanised warfare. The British first tanks were used during the Battle of the Somme on 15 September 1916. Mechanical reliability was an issue, but the experiment proved its worth. Within a year, the British were fielding tanks by the hundreds, and they showed their potential during the Battle of Cambrai in November 1917, by breaking the Hindenburg Line, while combined arms teams captured 8,000 enemy soldiers and 100 guns. Meanwhile, the French introduced the first tanks with a rotating turret, the Renault FT, which became a decisive tool of the victory. The conflict also saw the introduction of light automatic weapons and submachine guns, such as the Lewis Gun, the Browning automatic rifle, and the Bergmann MP18.British Vickers machine gun, 1917
Another new weapon, the flamethrower, was first used by the German army and later adopted by other forces. Although not of high tactical value, the flamethrower was a powerful, demoralising weapon that caused terror on the battlefield.
Trench railways evolved to supply the enormous quantities of food, water, and ammunition required to support large numbers of soldiers in areas where conventional transportation systems had been destroyed. Internal combustion engines and improved traction systems for automobiles and trucks/lorries eventually rendered trench railways obsolete.
Germany deployed U-boats (submarines) after the war began. Alternating between restricted and unrestricted submarine warfare in the Atlantic, the Kaiserliche Marine employed them to deprive the British Isles of vital supplies. The deaths of British merchant sailors and the seeming invulnerability of U-boats led to the development of depth charges (1916), hydrophones (passive sonar, 1917), blimps, hunter-killer submarines (HMS R-1, 1917), forward-throwing anti-submarine weapons, and dipping hydrophones (the latter two both abandoned in 1918).[86] To extend their operations, the Germans proposed supply submarines (1916). Most of these would be forgotten in the interwar period until World War II revived the need.[250]
Aviation
Main article: Aviation in World War IFixed-wing aircraft were first used militarily by the Italians in Libya on 23 October 1911 during the Italo-Turkish War for reconnaissance, soon followed by the dropping of grenades and aerial photography the next year. By 1914, their military utility was obvious. They were initially used for reconnaissance and ground attack. To shoot down enemy planes, anti-aircraft guns and fighter aircraft were developed. Strategic bombers were created, principally by the Germans and British, though the former used Zeppelins as well.[252] Towards the end of the conflict, aircraft carriers were used for the first time, with HMS Furious launching Sopwith Camels in a raid to destroy the Zeppelin hangars at Tondern in 1918.[253]RAF Sopwith Camel. In April 1917, the average life expectancy of a British pilot on the Western Front was 93 flying hours.[251]
Manned observation balloons, floating high above the trenches, were used as stationary reconnaissance platforms, reporting enemy movements and directing artillery. Balloons commonly had a crew of two, equipped with parachutes,[254] so that if there was an enemy air attack the crew could parachute to safety. At the time, parachutes were too heavy to be used by pilots of aircraft (with their marginal power output), and smaller versions were not developed until the end of the war; they were also opposed by the British leadership, who feared they might promote cowardice.[255]
Recognised for their value as observation platforms, balloons were important targets for enemy aircraft. To defend them against air attack, they were heavily protected by antiaircraft guns and patrolled by friendly aircraft; to attack them, unusual weapons such as air-to-air rockets were even tried. Thus, the reconnaissance value of blimps and balloons contributed to the development of air-to-air combat between all types of aircraft, and to the trench stalemate, because it was impossible to move large numbers of troops undetected. The Germans conducted air raids on England during 1915 and 1916 with airships, hoping to damage British morale and cause aircraft to be diverted from the front lines, and indeed the resulting panic led to the diversion of several squadrons of fighters from France.[252][255]
War crimes
Baralong incidents
Main article: Baralong incidentsOn 19 August 1915, the German submarine U-27 was sunk by the British Q-ship HMS Baralong. All German survivors were summarily executed by Baralong's crew on the orders of Lieutenant Godfrey Herbert, the captain of the ship. The shooting was reported to the media by American citizens who were on board the Nicosia, a British freighter loaded with war supplies, which was stopped by U-27 just minutes before the incident.[256]HMS Baralong.
On 24 September, Baralong destroyed U-41, which was in the process of sinking the cargo ship Urbino. According to Karl Goetz, the submarine's commander, Baralong continued to fly the US flag after firing on U-41 and then rammed the lifeboat – carrying the German survivors – sinking it.[257]
Torpedoing of HMHS Llandovery Castle
The Canadian hospital ship HMHS Llandovery Castle was torpedoed by the German submarine SM U-86 on 27 June 1918 in violation of international law. Only 24 of the 258 medical personnel, patients, and crew survived. Survivors reported that the U-boat surfaced and ran down the lifeboats, machine-gunning survivors in the water. The U-boat captain, Helmut Patzig, was charged with war crimes in Germany following the war, but escaped prosecution by going to the Free City of Danzig, beyond the jurisdiction of German courts.[258]
Chemical weapons in warfare
Main article: Chemical weapons in World War IThe first successful use of poison gas as a weapon of warfare occurred during the Second Battle of Ypres (22 April – 25 May 1915).[259] Gas was soon used by all major belligerents throughout the war. It is estimated that the use of chemical weapons employed by both sides throughout the war had inflicted 1.3 million casualties. For example, the British had over 180,000 chemical weapons casualties during the war, and up to one-third of American casualties were caused by them. The Russian Army reportedly suffered roughly 500,000 chemical weapon casualties in World War I.[260] The use of chemical weapons in warfare was in direct violation of the 1899 Hague Declaration Concerning Asphyxiating Gases and the 1907 Hague Convention on Land Warfare, which prohibited their use.[261][262]French soldiers making a gas and flame attack on German trenches in Flanders
The effect of poison gas was not limited to combatants. Civilians were at risk from the gases as winds blew the poison gases through their towns, and rarely received warnings or alerts of potential danger. In addition to absent warning systems, civilians often did not have access to effective gas masks. An estimated 100,000–260,000 civilian casualties were caused by chemical weapons during the conflict and tens of thousands more (along with military personnel) died from scarring of the lungs, skin damage, and cerebral damage in the years after the conflict ended. Many commanders on both sides knew such weapons would cause major harm to civilians but nonetheless continued to use them. British Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig wrote in his diary, "My officers and I were aware that such weapons would cause harm to women and children living in nearby towns, as strong winds were common in the battlefront. However, because the weapon was to be directed against the enemy, none of us were overly concerned at all."[263][264][265][266]
Genocide and ethnic cleansing
Armenians killed during the Armenian Genocide. Image taken from Ambassador Morgenthau's Story, written by Henry Morgenthau, Sr. and published in 1918.[267]The ethnic cleansing of the Ottoman Empire's Armenian population, including mass deportations and executions, during the final years of the Ottoman Empire is considered genocide.[269] The Ottomans carried out organized and systematic massacres of the Armenian population at the beginning of the war and portrayed deliberately provoked acts of Armenian resistance as rebellions to justify further extermination.[270] In early 1915, a number of Armenians volunteered to join the Russian forces and the Ottoman government used this as a pretext to issue the Tehcir Law (Law on Deportation), which authorized the deportation of Armenians from the Empire's eastern provinces to Syria between 1915 and 1918. The Armenians were intentionally marched to death and a number were attacked by Ottoman brigands.[271] While an exact number of deaths is unknown, the International Association of Genocide Scholars estimates 1.5 million.[269][272] The government of Turkey has consistently denied the genocide, arguing that those who died were victims of inter-ethnic fighting, famine, or disease during World War I; these claims are rejected by most historians.[273] Other ethnic groups were similarly attacked by the Ottoman Empire during this period, including Assyrians and Greeks, and some scholars consider those events to be part of the same policy of extermination.[274][275][276]Austro-Hungarian soldiers executing men and women in Serbia, 1916[268]
Russian Empire
Main article: Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian EmpireMany pogroms accompanied the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the ensuing Russian Civil War. 60,000–200,000 civilian Jews were killed in the atrocities throughout the former Russian Empire (mostly within the Pale of Settlement in present-day Ukraine).[277]
Rape of Belgium
Main article: Rape of BelgiumThe German invaders treated any resistance—such as sabotaging rail lines—as illegal and immoral, and shot the offenders and burned buildings in retaliation. In addition, they tended to suspect that most civilians were potential franc-tireurs (guerrillas) and, accordingly, took and sometimes killed hostages from among the civilian population. The German army executed over 6,500 French and Belgian civilians between August and November 1914, usually in near-random large-scale shootings of civilians ordered by junior German officers. The German Army destroyed 15,000–20,000 buildings—most famously the university library at Louvain—and generated a wave of refugees of over a million people. Over half the German regiments in Belgium were involved in major incidents.[278] Thousands of workers were shipped to Germany to work in factories. British propaganda dramatizing the Rape of Belgium attracted much attention in the United States, while Berlin said it was both lawful and necessary because of the threat of franc-tireurs like those in France in 1870.[279] The British and French magnified the reports and disseminated them at home and in the United States, where they played a major role in dissolving support for Germany.[280][281]
Soldiers' experiences
Main articles: List of last surviving World War I veterans by country, World War I casualties, Commonwealth War Graves Commission, and American Battle Monuments CommissionThe British soldiers of the war were initially volunteers but increasingly were conscripted into service. Surviving veterans, returning home, often found that they could only discuss their experiences amongst themselves. Grouping together, they formed "veterans' associations" or "Legions".The First Contingent of the Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps to the 1 Lincolns, training in Bermuda for the Western Front, winter 1914–1915. The two BVRC contingents suffered 75% casualties.
Prisoners of war
Main article: World War I prisoners of war in GermanyAbout eight million men surrendered and were held in POW camps during the war. All nations pledged to follow the Hague Conventions on fair treatment of prisoners of war, and the survival rate for POWs was generally much higher than that of their peers at the front.[282] Individual surrenders were uncommon; large units usually surrendered en masse. At the siege of Maubeuge about 40,000 French soldiers surrendered, at the battle of Galicia Russians took about 100,000 to 120,000 Austrian captives, at the Brusilov Offensive about 325,000 to 417,000 Germans and Austrians surrendered to Russians, at the Battle of Tannenberg 92,000 Russians surrendered. When the besieged garrison of Kaunas surrendered in 1915, some 20,000 Russians became prisoners, at the battle near Przasnysz (February–March 1915) 14,000 Germans surrendered to Russians, at the First Battle of the Marne about 12,000 Germans surrendered to the Allies. 25–31% of Russian losses (as a proportion of those captured, wounded, or killed) were to prisoner status; for Austria-Hungary 32%, for Italy 26%, for France 12%, for Germany 9%; for Britain 7%. Prisoners from the Allied armies totalled about 1.4 million (not including Russia, which lost 2.5–3.5 million men as prisoners). From the Central Powers about 3.3 million men became prisoners; most of them surrendered to Russians.[283] Germany held 2.5 million prisoners; Russia held 2.2–2.9 million; while Britain and France held about 720,000. Most were captured just before the Armistice. The United States held 48,000. The most dangerous moment was the act of surrender, when helpless soldiers were sometimes gunned down.[284][285] Once prisoners reached a camp, conditions were, in general, satisfactory (and much better than in World War II), thanks in part to the efforts of the International Red Cross and inspections by neutral nations. However, conditions were terrible in Russia: starvation was common for prisoners and civilians alike; about 15–20% of the prisoners in Russia died and in Central Powers imprisonment—8% of Russians.[286] In Germany, food was scarce, but only 5% died.[287][288][289]German prisoners in a French prison camp, during the later part of the war
The Ottoman Empire often treated POWs poorly.[290] Some 11,800 British Empire soldiers, most of them Indians, became prisoners after the Siege of Kut in Mesopotamia in April 1916; 4,250 died in captivity.[291] Although many were in a poor condition when captured, Ottoman officers forced them to march 1,100 kilometres (684 mi) to Anatolia. A survivor said: "We were driven along like beasts; to drop out was to die."[292] The survivors were then forced to build a railway through the Taurus Mountains.British prisoners guarded by Ottoman forces after the First Battle of Gaza in 1917.
In Russia, when the prisoners from the Czech Legion of the Austro-Hungarian army were released in 1917, they re-armed themselves and briefly became a military and diplomatic force during the Russian Civil War.
While the Allied prisoners of the Central Powers were quickly sent home at the end of active hostilities, the same treatment was not granted to Central Power prisoners of the Allies and Russia, many of whom served as forced labor, e.g., in France until 1920. They were released only after many approaches by the Red Cross to the Allied Supreme Council.[293] German prisoners were still being held in Russia as late as 1924.[294]
Military attachés and war correspondents
Military and civilian observers from every major power closely followed the course of the war. Many were able to report on events from a perspective somewhat akin to modern "embedded" positions within the opposing land and naval forces.
Support and opposition to the war
Support
In the Balkans, Yugoslav nationalists such as the leader, Ante Trumbić, strongly supported the war, desiring the freedom of Yugoslavs from Austria-Hungary and other foreign powers and the creation of an independent Yugoslavia. The Yugoslav Committee was formed in Paris on 30 April 1915 but shortly moved its office to London; Trumbić led the Committee.[295] In April 1918, the Rome Congress of Oppressed Nationalities met, including Czechoslovak, Italian, Polish, Transylvanian, and Yugoslav representatives who urged the Allies to support national self-determination for the peoples residing within Austria-Hungary.[296]Poster urging women to join the British war effort, published by the Young Women's Christian Association
In the Middle East, Arab nationalism soared in Ottoman territories in response to the rise of Turkish nationalism during the war, with Arab nationalist leaders advocating the creation of a pan-Arab state. In 1916, the Arab Revolt began in Ottoman-controlled territories of the Middle East in an effort to achieve independence.[297]
In East Africa, Iyasu V of Ethiopia was supporting the Dervish state who were at war with the British in the Somaliland Campaign.[298] Von Syburg, German envoy in Addis Ababa said "now the time has come for Ethiopia to regain the coast of the Red Sea driving the Italians home, to restore the Empire to its ancient size." The Ethiopian Empire was on the verge of entering World War I on the side of the Central Powers before, Iyasu's overthrow due to Allied pressure on the Ethiopian aristocracy.[299]
A number of socialist parties initially supported the war when it began in August 1914.[296] But European socialists split on national lines, with the concept of class conflict held by radical socialists such as Marxists and syndicalists being overborne by their patriotic support for war.[300] Once the war began, Austrian, British, French, German, and Russian socialists followed the rising nationalist current by supporting their countries' intervention in the war.[301]
Italian nationalism was stirred by the outbreak of the war and was initially strongly supported by a variety of political factions. One of the most prominent and popular Italian nationalist supporters of the war was Gabriele d'Annunzio, who promoted Italian irredentism and helped sway the Italian public to support intervention in the war.[302] The Italian Liberal Party, under the leadership of Paolo Boselli, promoted intervention in the war on the side of the Allies and utilised the Dante Alighieri Society to promote Italian nationalism.[303] Italian socialists were divided on whether to support the war or oppose it; some were militant supporters of the war, including Benito Mussolini and Leonida Bissolati.[304] However, the Italian Socialist Party decided to oppose the war after anti-militarist protestors were killed, resulting in a general strike called Red Week.[305] The Italian Socialist Party purged itself of pro-war nationalist members, including Mussolini.[305] Mussolini, a syndicalist who supported the war on grounds of irredentist claims on Italian-populated regions of Austria-Hungary, formed the pro-interventionist Il Popolo d'Italia and the Fasci Rivoluzionario d'Azione Internazionalista ("Revolutionary Fasci for International Action") in October 1914 that later developed into the Fasci di Combattimento in 1919, the origin of fascism.[306] Mussolini's nationalism enabled him to raise funds from Ansaldo (an armaments firm) and other companies to create Il Popolo d'Italia to convince socialists and revolutionaries to support the war.[307]
Opposition
Main articles: Opposition to World War I and French Army MutiniesOnce war was declared, many socialists and trade unions backed their governments. Among the exceptions were the Bolsheviks, the Socialist Party of America, and the Italian Socialist Party, and individuals such as Karl Liebknecht, Rosa Luxemburg, and their followers in Germany.The Deserter, 1916. Anti-war cartoon depicting Jesus facing a firing squad with soldiers from five European countries.
Benedict XV, elected to the papacy less than three months into World War I, made the war and its consequences the main focus of his early pontificate. In stark contrast to his predecessor,[308] five days after his election he spoke of his determination to do what he could to bring peace. His first encyclical, Ad beatissimi Apostolorum, given 1 November 1914, was concerned with this subject. Benedict XV found his abilities and unique position as a religious emissary of peace ignored by the belligerent powers. The 1915 Treaty of London between Italy and the Triple Entente included secret provisions whereby the Allies agreed with Italy to ignore papal peace moves towards the Central Powers. Consequently, the publication of Benedict's proposed seven-point Peace Note of August 1917 was roundly ignored by all parties except Austria-Hungary.[309]
In Britain, in 1914, the Public Schools Officers' Training Corps annual camp was held at Tidworth Pennings, near Salisbury Plain. Head of the British Army, Lord Kitchener, was to review the cadets, but the imminence of the war prevented him. General Horace Smith-Dorrien was sent instead. He surprised the two-or-three thousand cadets by declaring (in the words of Donald Christopher Smith, a Bermudian cadet who was present),
that war should be avoided at almost any cost, that war would solve nothing, that the whole of Europe and more besides would be reduced to ruin, and that the loss of life would be so large that whole populations would be decimated. In our ignorance I, and many of us, felt almost ashamed of a British General who uttered such depressing and unpatriotic sentiments, but during the next four years, those of us who survived the holocaust—probably not more than one-quarter of us—learned how right the General's prognosis was and how courageous he had been to utter it.[310]
Voicing these sentiments did not hinder Smith-Dorrien's career, or prevent him from doing his duty in World War I to the best of his abilities.
Many countries jailed those who spoke out against the conflict. These included Eugene Debs in the United States and Bertrand Russell in Britain. In the US, the Espionage Act of 1917 and Sedition Act of 1918 made it a federal crime to oppose military recruitment or make any statements deemed "disloyal". Publications at all critical of the government were removed from circulation by postal censors,[149] and many served long prison sentences for statements of fact deemed unpatriotic.Possible execution at Verdun at the time of the mutinies in 1917. The original French text accompanying this photograph notes however that the uniforms are those of 1914/15 and that the execution may be that of a spy at the beginning of the war.
A number of nationalists opposed intervention, particularly within states that the nationalists were hostile to. Although the vast majority of Irish people consented to participate in the war in 1914 and 1915, a minority of advanced Irish nationalists staunchly opposed taking part.[311] The war began amid the Home Rule crisis in Ireland that had resurfaced in 1912 and, by July 1914, there was a serious possibility of an outbreak of civil war in Ireland. Irish nationalists and Marxists attempted to pursue Irish independence, culminating in the Easter Rising of 1916, with Germany sending 20,000 rifles to Ireland to stir unrest in Britain.[312] The UK government placed Ireland under martial law in response to the Easter Rising; although, once the immediate threat of revolution had dissipated, the authorities did try to make concessions to nationalist feeling.[313]
Other opposition came from conscientious objectors—some socialist, some religious—who refused to fight. In Britain, 16,000 people asked for conscientious objector status.[314] Some of them, most notably prominent peace activist Stephen Henry Hobhouse, refused both military and alternative service.[315] Many suffered years of prison, including solitary confinement and bread and water diets. Even after the war, in Britain many job advertisements were marked "No conscientious objectors need apply".
The Central Asian Revolt started in the summer of 1916, when the Russian Empire government ended its exemption of Muslims from military service.[316]
In 1917, a series of French Army Mutinies led to dozens of soldiers being executed and many more imprisoned.
In Milan, in May 1917, Bolshevik revolutionaries organised and engaged in rioting calling for an end to the war, and managed to close down factories and stop public transportation.[317] The Italian army was forced to enter Milan with tanks and machine guns to face Bolsheviks and anarchists, who fought violently until 23 May when the army gained control of the city. Almost 50 people (including three Italian soldiers) were killed and over 800 people arrested.[317]German Revolution, Kiel, 1918
In September 1917, Russian soldiers in France began questioning why they were fighting for the French at all and mutinied.[318] In Russia, opposition to the war led to soldiers also establishing their own revolutionary committees, which helped foment the October Revolution of 1917, with the call going up for "bread, land, and peace". The Bolsheviks agreed to a peace treaty with Germany, the peace of Brest-Litovsk, despite its harsh conditions.
In northern Germany, the end of October 1918 saw the beginning of the German Revolution of 1918–1919. Units of the German Navy refused to set sail for a last, large-scale operation in a war which they saw as good as lost; this initiated the uprising. The sailors' revolt which then ensued in the naval ports of Wilhelmshaven and Kiel spread across the whole country within days and led to the proclamation of a republic on 9 November 1918 and shortly thereafter to the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II.
Conscription
Conscription was common in most European countries. However it was controversial in English speaking countries. It was especially unpopular among minority ethnic groups—especially the Irish Catholics in Ireland[319] and Australia, and the French Catholics in Canada. In Canada the issue produced a major political crisis that permanently alienated the Francophiles. It opened a political gap between French Canadians, who believed their true loyalty was to Canada and not to the British Empire, and members of the Anglophone majority, who saw the war as a duty to their British heritage.[320] In Australia, a sustained pro-conscription campaign by Billy Hughes, the Prime Minister, caused a split in the Australian Labor Party, so Hughes formed the Nationalist Party of Australia in 1917 to pursue the matter. Farmers, the labour movement, the Catholic Church, and the Irish Catholics successfully opposed Hughes' push, which was rejected in two plebiscites.[321]Young men registering for conscription, New York City, 5 June 1917
In Britain, conscription resulted in the calling up of nearly every physically fit man in Britain—six of ten million eligible. Of these, about 750,000 lost their lives. Most deaths were to young unmarried men; however, 160,000 wives lost husbands and 300,000 children lost fathers.[322] In the United States, conscription began in 1917 and was generally well received, with a few pockets of opposition in isolated rural areas.[323]
Diplomacy
Main article: Diplomatic history of World War Ithe non-military diplomatic and propaganda interactions among the nations were designed to build support for the cause, or to undermine support for the enemy. For the most part, wartime diplomacy focused on five issues: propaganda campaigns; defining and redefining the war goals, which became harsher as the war went on; luring neutral nations (Italy, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, Romania) into the coalition by offering slices of enemy territory; and encouragement by the Allies of nationalistic minority movements inside the Central Powers, especially among Czechs, Poles, and Arabs. In addition, there were multiple peace proposals coming from neutrals, or one side or the other; none of them progressed very far.[324][325][326]
Legacy and memory
The first tentative efforts to comprehend the meaning and consequences of modern warfare began during the initial phases of the war, and this process continued throughout and after the end of hostilities, and is still underway, more than a century later.... "Strange, friend," I said, "Here is no cause to mourn."
"None," said the other, "Save the undone years"...
— Wilfred Owen, Strange Meeting, 1918[245]
Historiography
Historian Heather Jones argues that the historiography has been reinvigorated by the cultural turn in recent years. Scholars have raised entirely new questions regarding military occupation, radicalization of politics, race, and the male body. Furthermore, new research has revised our understanding of five major topics that historians have long debated. These are: Why did the war begin? Why did the Allies win? Were the generals to blame for the high casualty rates? How did the soldiers endure the horrors of trench warfare? To what extent did the civilian homefront accept and endorse the war effort?[327]
Memorials
A typical village war memorial to soldiers killed in World War IMain article: World War I memorialsMemorials were erected in thousands of villages and towns. Close to battlefields, those buried in improvised burial grounds were gradually moved to formal graveyards under the care of organisations such as the Commonwealth War Graves Commission, the American Battle Monuments Commission, the German War Graves Commission, and Le Souvenir français. Many of these graveyards also have central monuments to the missing or unidentified dead, such as the Menin Gate memorial and the Thiepval Memorial to the Missing of the Somme.
In 1915 John McCrae, a Canadian army doctor, wrote the poem In Flanders Fields as a salute to those who perished in the Great War. Published in Punch on 8 December 1915, it is still recited today, especially on Remembrance Day and Memorial Day.[328][329]
National World War I Museum and Memorial in Kansas City, Missouri, is a memorial dedicated to all Americans who served in World War I. The Liberty Memorial was dedicated on 1 November 1921, when the supreme Allied commanders spoke to a crowd of more than 100,000 people.[330]
The UK Government has budgeted substantial resources to the commemoration of the war during the period 2014 to 2018. The lead body is the Imperial War Museum.[331] On 3 August 2014, French President Francois Hollande and German President Joachim Gauck together marked the centenary of Germany's declaration of war on France by laying the first stone of a memorial in Vieil Armand, known in German as Hartmannswillerkopf, for French and German soldiers killed in the war.[332]
Cultural memory
Further information: World War I in popular cultureWorld War I had a lasting impact on social memory. It was seen by many in Britain as signalling the end of an era of stability stretching back to the Victorian period, and across Europe many regarded it as a watershed.[333] Historian Samuel Hynes explained:
A generation of innocent young men, their heads full of high abstractions like Honour, Glory and England, went off to war to make the world safe for democracy. They were slaughtered in stupid battles planned by stupid generals. Those who survived were shocked, disillusioned and embittered by their war experiences, and saw that their real enemies were not the Germans, but the old men at home who had lied to them. They rejected the values of the society that had sent them to war, and in doing so separated their own generation from the past and from their cultural inheritance.[334]
This has become the most common perception of World War I, perpetuated by the art, cinema, poems, and stories published subsequently. Films such as All Quiet on the Western Front, Paths of Glory and King & Country have perpetuated the idea, while war-time films including Camrades, Poppies of Flanders, and Shoulder Arms indicate that the most contemporary views of the war were overall far more positive.[335] Likewise, the art of Paul Nash, John Nash, Christopher Nevinson, and Henry Tonks in Britain painted a negative view of the conflict in keeping with the growing perception, while popular war-time artists such as Muirhead Bone painted more serene and pleasant interpretations subsequently rejected as inaccurate.[334] Several historians like John Terraine, Niall Ferguson and Gary Sheffield have challenged these interpretations as partial and polemical views:
These beliefs did not become widely shared because they offered the only accurate interpretation of wartime events. In every respect, the war was much more complicated than they suggest. In recent years, historians have argued persuasively against almost every popular cliché of World War I. It has been pointed out that, although the losses were devastating, their greatest impact was socially and geographically limited. The many emotions other than horror experienced by soldiers in and out of the front line, including comradeship, boredom, and even enjoyment, have been recognised. The war is not now seen as a 'fight about nothing', but as a war of ideals, a struggle between aggressive militarism and more or less liberal democracy. It has been acknowledged that British generals were often capable men facing difficult challenges, and that it was under their command that the British army played a major part in the defeat of the Germans in 1918: a great forgotten victory.[335]
Though these views have been discounted as "myths",[334][336] they are common. They have dynamically changed according to contemporary influences, reflecting in the 1950s perceptions of the war as "aimless" following the contrasting Second World War and emphasising conflict within the ranks during times of class conflict in the 1960s. The majority of additions to the contrary are often rejected.[335]
Social trauma
The social trauma caused by unprecedented rates of casualties manifested itself in different ways, which have been the subject of subsequent historical debate.[337]A 1919 book for veterans, from the US War Department
The optimism of la belle époque was destroyed, and those who had fought in the war were referred to as the Lost Generation.[338] For years afterwards, people mourned the dead, the missing, and the many disabled.[339] Many soldiers returned with severe trauma, suffering from shell shock (also called neurasthenia, a condition related to posttraumatic stress disorder).[340] Many more returned home with few after-effects; however, their silence about the war contributed to the conflict's growing mythological status. Though many participants did not share in the experiences of combat or spend any significant time at the front, or had positive memories of their service, the images of suffering and trauma became the widely shared perception. Such historians as Dan Todman, Paul Fussell, and Samuel Heyns have all published works since the 1990s arguing that these common perceptions of the war are factually incorrect.[337]
Discontent in Germany
The rise of Nazism and Fascism included a revival of the nationalist spirit and a rejection of many post-war changes. Similarly, the popularity of the stab-in-the-back legend (German: Dolchstoßlegende) was a testament to the psychological state of defeated Germany and was a rejection of responsibility for the conflict. This conspiracy theory of betrayal became common, and the German populace came to see themselves as victims. The widespread acceptance of the "stab-in-the-back" theory delegitimized the Weimar government and destabilized the system, opening it to extremes of right and left.
Communist and fascist movements around Europe drew strength from this theory and enjoyed a new level of popularity. These feelings were most pronounced in areas directly or harshly affected by the war. Adolf Hitler was able to gain popularity by utilising German discontent with the still controversial Treaty of Versailles.[341] World War II was in part a continuation of the power struggle never fully resolved by World War I. Furthermore, it was common for Germans in the 1930s to justify acts of aggression due to perceived injustices imposed by the victors of World War I.[342][343][344] American historian William Rubinstein wrote that:
The 'Age of Totalitarianism' included nearly all of the infamous examples of genocide in modern history, headed by the Jewish Holocaust, but also comprising the mass murders and purges of the Communist world, other mass killings carried out by Nazi Germany and its allies, and also the Armenian Genocide of 1915. All these slaughters, it is argued here, had a common origin, the collapse of the elite structure and normal modes of government of much of central, eastern and southern Europe as a result of World War I, without which surely neither Communism nor Fascism would have existed except in the minds of unknown agitators and crackpots.[345]
Economic effects
See also: Economic history of World War IOne of the most dramatic effects of the war was the expansion of governmental powers and responsibilities in Britain, France, the United States, and the Dominions of the British Empire. To harness all the power of their societies, governments created new ministries and powers. New taxes were levied and laws enacted, all designed to bolster the war effort; many have lasted to this day. Similarly, the war strained the abilities of some formerly large and bureaucratised governments, such as in Austria-Hungary and Germany.Poster showing women workers, 1915
Gross domestic product (GDP) increased for three Allies (Britain, Italy, and US), but decreased in France and Russia, in neutral Netherlands, and in the three main Central Powers. The shrinkage in GDP in Austria, Russia, France, and the Ottoman Empire ranged between 30% and 40%. In Austria, for example, most pigs were slaughtered, so at war's end there was no meat.
In all nations, the government's share of GDP increased, surpassing 50% in both Germany and France and nearly reaching that level in Britain. To pay for purchases in the United States, Britain cashed in its extensive investments in American railroads and then began borrowing heavily on Wall Street. President Wilson was on the verge of cutting off the loans in late 1916, but allowed a great increase in US government lending to the Allies. After 1919, the US demanded repayment of these loans. The repayments were, in part, funded by German reparations which, in turn, were supported by American loans to Germany. This circular system collapsed in 1931 and the loans were never repaid. Britain still owed the United States $4.4 billion[346] of World War I debt in 1934, and this money was never repaid.[347]
Macro- and micro-economic consequences devolved from the war. Families were altered by the departure of many men. With the death or absence of the primary wage earner, women were forced into the workforce in unprecedented numbers. At the same time, industry needed to replace the lost labourers sent to war. This aided the struggle for voting rights for women.[348]
World War I further compounded the gender imbalance, adding to the phenomenon of surplus women. The deaths of nearly one million men during the war in Britain increased the gender gap by almost a million: from 670,000 to 1,700,000. The number of unmarried women seeking economic means grew dramatically. In addition, demobilisation and economic decline following the war caused high unemployment. The war increased female employment; however, the return of demobilised men displaced many from the workforce, as did the closure of many of the wartime factories.
In Britain, rationing was finally imposed in early 1918, limited to meat, sugar, and fats (butter and margarine), but not bread. The new system worked smoothly. From 1914 to 1918, trade union membership doubled, from a little over four million to a little over eight million.
Britain turned to her colonies for help in obtaining essential war materials whose supply from traditional sources had become difficult. Geologists such as Albert Ernest Kitson were called on to find new resources of precious minerals in the African colonies. Kitson discovered important new deposits of manganese, used in munitions production, in the Gold Coast.[349]
Article 231 of the Treaty of Versailles (the so-called "war guilt" clause) stated Germany accepted responsibility for "all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by the aggression of Germany and her allies."[350] It was worded as such to lay a legal basis for reparations, and a similar clause was inserted in the treaties with Austria and Hungary. However neither of them interpreted it as an admission of war guilt."[351] In 1921, the total reparation sum was placed at 132 billion gold marks. However, "Allied experts knew that Germany could not pay" this sum. The total sum was divided into three categories, with the third being "deliberately designed to be chimerical" and its "primary function was to mislead public opinion ... into believing the "total sum was being maintained."[352] Thus, 50 billion gold marks (12.5 billion dollars) "represented the actual Allied assessment of German capacity to pay" and "therefore ... represented the total German reparations" figure that had to be paid.[352]
This figure could be paid in cash or in kind (coal, timber, chemical dyes, etc.). In addition, some of the territory lost—via the treaty of Versailles—was credited towards the reparation figure as were other acts such as helping to restore the Library of Louvain.[353] By 1929, the Great Depression arrived, causing political chaos throughout the world.[354] In 1932 the payment of reparations was suspended by the international community, by which point Germany had only paid the equivalent of 20.598 billion gold marks in reparations.[355] With the rise of Adolf Hitler, all bonds and loans that had been issued and taken out during the 1920s and early 1930s were cancelled. David Andelman notes "refusing to pay doesn't make an agreement null and void. The bonds, the agreement, still exist." Thus, following the Second World War, at the London Conference in 1953, Germany agreed to resume payment on the money borrowed. On 3 October 2010, Germany made the final payment on these bonds.[i]
See also
- Outline of World War I
- Death rates in the 20th century
- Diplomatic history of World War I
- European Civil War
- List of people associated with World War I
- Lists of wars
- List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll
- Lists of World War I topics
- Timeline of World War I
- World War I casualties
- World War I medal abbreviations
Footnotes
- The United States did not ratify any of the treaties agreed to at the Paris Peace Conference.
Notes
- MacMillan, Margaret (25 December 2010). "Ending the War to End All Wars". The New York Times. New York. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
NOT many people noticed at the time, but World War I ended this year.
References
- For a comprehensive bibliography see List of books about World War I
- American Battle Monuments Commission (1938), American Armies and Battlefields in Europe: A History, Guide, and Reference Book, US Government Printing Office, OCLC 59803706
- Army Art of World War I, United States Army Center of Military History: Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of American History, 1993, OCLC 28608539
- Ayers, Leonard Porter (1919). The War with Germany: A Statistical Summary. Government Printing Office.
- Bade, Klaus J; Brown, Allison (tr.) (2003), Migration in European History, The making of Europe, Oxford: Blackwell, ISBN 0-631-18939-4, OCLC 52695573 (translated from the German)
- Balakian, Peter (2003), The Burning Tigris: The Armenian Genocide and America's Response, New York: HarperCollins, ISBN 978-0-06-019840-4, OCLC 56822108
- Ball, Alan M (1996), And Now My Soul Is Hardened: Abandoned Children in Soviet Russia, 1918–1930, Berkeley: University of California Press, ISBN 978-0-520-20694-6, reviewed in Hegarty, Thomas J (March–June 1998). "And Now My Soul Is Hardened: Abandoned Children in Soviet Russia, 1918–1930". Canadian Slavonic Papers. (via Highbeam.com)
- Bass, Gary Jonathan (2002), Stay the Hand of Vengeance: The Politics of War Crimes Tribunals, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, pp. 424pp, ISBN 0-691-09278-8, OCLC 248021790
- Blair, Dale (2005), No Quarter: Unlawful Killing and Surrender in the Australian War Experience, 1915–1918, Charnwood, Australia: Ginninderra Press, ISBN 1-74027-291-9, OCLC 62514621
- Brands, Henry William (1997), T. R.: The Last Romantic, New York: Basic Books, ISBN 0-465-06958-4, OCLC 36954615
- Braybon, Gail (2004). Evidence, History, and the Great War: Historians and the Impact of 1914–18. Berghahn Books. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-57181-801-0.
- Brown, Judith M. (1994), Modern India: The Origins of an Asian Democracy, Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-873113-2
- Chickering, Rodger (2004), Imperial Germany and the Great War, 1914–1918, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-83908-4, OCLC 55523473
- Clark, Charles Upson (1927), Bessarabia, Russia and Roumania on the Black Sea, New York: Dodd, Mead, OCLC 150789848
- Clark, Christopher (2014), The Sleepwalkers: How Europe Went to War in 1914, New York: Harper Books, ISBN 978-0-06-114666-4
- Cockfield, Jamie H (1997), With snow on their boots : The tragic odyssey of the Russian Expeditionary Force in France during World War I, Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 0-312-22082-0
- Conlon, Joseph M, The historical impact of epidemic typhus (PDF), Montana State University, retrieved 21 April 2009
- Cook, Tim (2006), "The politics of surrender: Canadian soldiers and the killing of prisoners in the First World War", The Journal of Military History, 70 (3): 637–665, doi:10.1353/jmh.2006.0158
- Cross, Wilbur L (1991), Zeppelins of World War I, New York: Paragon Press, ISBN 978-1-55778-382-0, OCLC 22860189
- Crowe, David (2001). The Essentials of European History: 1914 to 1935, World War I and Europe in crisis. Research and Education Association. ISBN 978-0-87891-710-5.
- DiNardo, Richard (2015). Invasion: The Conquest of Serbia, 1915. Santa Barbara, California: Praeger. ISBN 978-1-4408-0092-4.
- Djokić, Dejan (2003), Yugoslavism : histories of a failed idea, 1918–1992, London: Hurst, OCLC 51093251
- Doughty, Robert A. (2005), Pyrrhic victory: French strategy and operations in the Great War, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-01880-8
- Duffy, Michael, Somme, First World War.com, ISBN 0-297-84689-2, retrieved 25 February 2007
- Dupuy, R. Ernest and Trevor N. (1993), The Harper's Encyclopedia of Military History, 4th Edition, Harper Collins Publishers, ISBN 978-0-06-270056-8
- Encyclopædia Britannica (12th ed. 1922) comprises the 11th edition plus three new volumes 30-31-32 that cover events since 1911 with thorough coverage of the war as well as every country and colony. partly online and list of article titles
- Evans, David (2004), The First World War, Teach yourself, London: Hodder Arnold, ISBN 0-340-88489-4, OCLC 224332259
- Evans, Leslie (27 May 2005), Future of Iraq, Israel-Palestine Conflict, and Central Asia Weighed at International Conference, UCLA International Institute, retrieved 30 December 2008
- Falls, Cyril Bentham (1960), The First World War, London: Longmans, ISBN 1-84342-272-7, OCLC 460327352
- Farwell, Byron (1989), The Great War in Africa, 1914–1918, W.W. Norton, ISBN 978-0-393-30564-7
- Ferguson, Niall (1999), The Pity of War, New York: Basic Books, pp. 563pp, ISBN 0-465-05711-X, OCLC 41124439
- Ferguson, Niall (2006), The War of the World: Twentieth-Century Conflict and the Descent of the West, New York: Penguin Press, ISBN 1-59420-100-5
- Fortescue, Granville Roland (28 October 1915), "London in Gloom over Gallipoli; Captain Fortescue in Book and Ashmead-Bartlett in Lecture Declare Campaign Lost", New York Times
- Fromkin, David (1989). A Peace to End All Peace: The Fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Creation of the Modern Middle East. New York: Henry Holt and Co. ISBN 0-8050-0857-8.
- Fromkin, David (2004), Europe's Last Summer: Who Started the Great War in 1914?, New York: Alfred A. Knopf, ISBN 0-375-41156-9, OCLC 53937943
- Gelvin, James L (2005), The Israel-Palestine Conflict: One Hundred Years of War, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-85289-7, OCLC 59879560
- Grant, R.G. (2005), Battle: A Visual Journey Through 5,000 Years of Combat, DK Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7566-5578-5
- Gray, Randal; Argyle, Christopher (1990), Chronicle of the First World War, New York: Facts on File, ISBN 978-0-8160-2595-4, OCLC 19398100
- Gilbert, Martin (1994), First World War, Stoddart Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7737-2848-6
- Gilbert, Martin (2004), The First World War: A Complete History, Clearwater, Florida: Owl Books, p. 306, ISBN 0-8050-7617-4, OCLC 34792651
- Goodspeed, Donald James (1985), The German Wars 1914–1945, New York: Random House; Bonanza, ISBN 978-0-517-46790-9
- Gray, Randal (1991), Kaiserschlacht 1918: the final German offensive, Osprey, ISBN 978-1-85532-157-1
- Green, John Frederick Norman (1938), "Obituary: Albert Ernest Kitson", Geological Society Quarterly Journal, Geological Society, 94
- Halpern, Paul G (1995), A Naval History of World War I, New York: Routledge, ISBN 1-85728-498-4, OCLC 60281302
- Harris, J. P. (2008), Douglas Haig and the First World War (2009 ed.), Cambridge: CUP, ISBN 978-0-521-89802-7
- Hartcup, Guy (1988), The War of Invention; Scientific Developments, 1914–18, Brassey's Defence Publishers, ISBN 0-08-033591-8
- Havighurst, Alfred F (1985), Britain in transition: the twentieth century (4 ed.), University of Chicago Press, ISBN 978-0-226-31971-1
- Heller, Charles E (1984), Chemical warfare in World War I : the American experience, 1917–1918, Fort Leavenworth, Kansas: Combat Studies Institute, OCLC 123244486
- Heyman, Neil M (1997), World War I, Guides to historic events of the twentieth century, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press, ISBN 0-313-29880-7, OCLC 36292837
- Hickey, Michael (2003), The Mediterranean Front 1914–1923, The First World War, 4, New York: Routledge, pp. 60–65, ISBN 0-415-96844-5, OCLC 52375688
- Hinterhoff, Eugene (1984), Young, Peter, ed., "The Campaign in Armenia", Marshall Cavendish Illustrated Encyclopedia of World War I, New York: Marshall Cavendish, ii, ISBN 0-86307-181-3
- Hirschfeld, Gerhard et al. eds. Brill's Encyclopedia of the First World War (2012), 1105pp
- Hooker, Richard (1996), The Ottomans, Washington State University, archived from the original on 8 October 1999
- Hooker, Richard (1996), The Ottomans, Washington State University, archived from the original on 8 October 1999
- Horne, John; Kramer, Alan (2001), German Atrocities, 1914: A History of Denial, Yale University Press, OCLC 47181922
- Hovannisian, Richard G. (1967), Armenia on the Road to Independence, 1918, Berkeley: University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-00574-0
- Hull, Isabel Virginia (2006), Absolute destruction: military culture and the practices of war in Imperial Germany, Cornell University Press, ISBN 978-0-8014-7293-0
- Humphries, Mark Osborne (2007), ""Old Wine in New Bottles": A Comparison of British and Canadian Preparations for the Battle of Arras", in Hayes, Geoffrey; Iarocci, Andrew; Bechthold, Mike, Vimy Ridge: A Canadian Reassessment, Waterloo: Wilfrid Laurier University Press, pp. 65–85, ISBN 0-88920-508-6
- Inglis, David (1995), Vimy Ridge: 1917–1992, A Canadian Myth over Seventy Five Years (PDF), Burnaby: Simon Fraser University
- Isaac, Jad; Hosh, Leonardo (7–9 May 1992), Roots of the Water Conflict in the Middle East, University of Waterloo, archived from the original on 28 September 2006[dead link]
- Jenkins, Burris A (2009), Facing the Hindenburg Line, BiblioBazaar, ISBN 978-1-110-81238-7
- Johnson, James Edgar (2001), Full Circle: The Story of Air Fighting, London: Cassell, ISBN 0-304-35860-6, OCLC 45991828
- Jones, Howard (2001), Crucible of Power: A History of US Foreign Relations Since 1897, Wilmington, Delaware: Scholarly Resources Books, ISBN 0-8420-2918-4, OCLC 46640675
- Kaplan, Robert D (February 1993), "Syria: Identity Crisis", The Atlantic, retrieved 30 December 2008
- Karp, Walter (1979), The Politics of War (1st ed.), ISBN 0-06-012265-X, OCLC 4593327, Wilson's maneuvering US into war
- Keegan, John (1998), The First World War, Hutchinson, ISBN 0-09-180178-8, general military history
- Keene, Jennifer D (2006), World War I, Daily Life Through History Series, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press, p. 5, ISBN 0-313-33181-2, OCLC 70883191
- Kernek, Sterling (December 1970), "The British Government's Reactions to President Wilson's 'Peace' Note of December 1916", The Historical Journal, 13 (4): 721–766, doi:10.1017/S0018246X00009481, JSTOR 2637713
- Kitchen, Martin (2000) [1980], Europe Between the Wars, New York: Longman, ISBN 0-582-41869-0, OCLC 247285240
- Knobler, Stacey L, ed. (2005), The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary, Washington DC: National Academies Press, ISBN 0-309-09504-2, OCLC 57422232
- Kurlander, Eric (2006), Steffen Bruendel. Volksgemeinschaft oder Volksstaat: Die "Ideen von 1914" und die Neuordnung Deutschlands im Ersten Weltkrieg (Book review), H-net, retrieved 17 November 2009
- Lehmann, Hartmut; van der Veer, Peter, eds. (1999), Nation and religion: perspectives on Europe and Asia, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, ISBN 0-691-01232-6, OCLC 39727826
- Love, Dave (May 1996), "The Second Battle of Ypres, April 1915", Sabretasche, 26 (4)
- Lyons, Michael J (1999), World War I: A Short History (2nd ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-020551-6
- Ludendorff, Erich (1919), My War Memories, 1914–1918, OCLC 60104290 also published by Harper as "Ludendorff's Own Story, August 1914 – November 1918: The Great War from the Siege of Liège to the Signing of the Armistice as Viewed from the Grand Headquarters of the German Army" OCLC 561160 (original title Meine Kriegserinnerungen, 1914–1918)
- Magliveras, Konstantinos D (1999), Exclusion from Participation in International Organisations: The Law and Practice behind Member States' Expulsion and Suspension of Membership, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, ISBN 90-411-1239-1
- Martel, Gordon (2003), The Origins of the First World War, Pearson Longman, Harlow
- Mawdsley, Evan (2008), The Russian Civil War (Edinburgh ed.), Birlinn location, ISBN 1-84341-041-9
- McLellan, Edwin N, The United States Marine Corps in the World War
- Meyer, Gerald J (2006), A World Undone: The Story of the Great War 1914 to 1918, Random House, ISBN 978-0-553-80354-9
- Millett, Allan Reed; Murray, Williamson (1988), Military Effectiveness, Boston: Allen Unwin, ISBN 0-04-445053-2, OCLC 220072268
- Moon, John Ellis van Courtland (July 1996), "United States Chemical Warfare Policy in World War II: A Captive of Coalition Policy?", The Journal of Military History, Society for Military History, 60 (3): 495–511, doi:10.2307/2944522, JSTOR 2944522
- Morton, Desmond (1992), Silent Battle: Canadian Prisoners of War in Germany, 1914–1919, Toronto: Lester Publishing, ISBN 1-895555-17-5, OCLC 29565680
- Mosier, John (2001), "Germany and the Development of Combined Arms Tactics", Myth of the Great War: How the Germans Won the Battles and How the Americans Saved the Allies, New York: Harper Collins, ISBN 0-06-019676-9
- Muller, Jerry Z (March–April 2008), "Us and Them – The Enduring Power of Ethnic Nationalism", Foreign Affairs, Council on Foreign Relations, retrieved 30 December 2008
- Neiberg, Michael S (2005), Fighting the Great War: A Global History, Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-01696-3, OCLC 56592292
- Nicholson, Gerald WL (1962), Canadian Expeditionary Force, 1914–1919: Official History of the Canadian Army in the First World War (1st ed.), Ottawa: Queens Printer and Controller of Stationary, OCLC 2317262, archived from the original on 16 May 2007[dead link]
- Northedge, FS (1986), The League of Nations: Its Life and Times, 1920–1946, New York: Holmes & Meier, ISBN 0-7185-1316-9
- Page, Thomas Nelson, Italy and the World War, Brigham Young University, Chapter XI cites "Cf. articles signed XXX in La Revue de Deux Mondes, 1 and 15 March 1920"
- Painter, David S. (2012), "Oil and the American Century" (PDF), The Journal of American History, 99 (1): 24–39, doi:10.1093/jahist/jas073
- Phillimore, George Grenville; Bellot, Hugh HL (1919), "Treatment of Prisoners of War", Transactions of the Grotius Society, 5: 47–64, OCLC 43267276
- Pitt, Barrie (2003), 1918: The Last Act, Barnsley: Pen and Sword, ISBN 0-85052-974-3, OCLC 56468232
- Price, Alfred (1980), Aircraft versus Submarine: the Evolution of the Anti-submarine Aircraft, 1912 to 1980, London: Jane's Publishing, ISBN 0-7106-0008-9, OCLC 10324173 Deals with technical developments, including the first dipping hydrophones
- Prior, Robin (1999), The First World War, London: Cassell, ISBN 0-304-35256-X
- Raudzens, George (October 1990), "War-Winning Weapons: The Measurement of Technological Determinism in Military History", The Journal of Military History, Society for Military History, 54 (4): 403–434, doi:10.2307/1986064, JSTOR 1986064
- Repington, Charles à Court (1920), The First World War, 1914–1918, 2, London: Constable, ISBN 1-113-19764-1
- Rickard, J (5 March 2001), "Erich von Ludendorff [sic], 1865–1937, German General", Military History Encyclopedia on the Web, HistoryOfWar.org, retrieved 6 February 2008
- Rickard, J (27 August 2007), The Ludendorff Offensives, 21 March-18 July 1918
- Roden, Mike, "The Lost Generation – myth and reality", Aftermath – when the boys came home, retrieved 6 November 2009
- Saadi, Abdul-Ilah (12 February 2009), Dreaming of Greater Syria, Al Jazeera, retrieved 14 August 2014
- Sachar, Howard Morley (1970), The emergence of the Middle East, 1914–1924, Allen Lane, ISBN 0-7139-0158-6, OCLC 153103197
- Salibi, Kamal Suleiman (1993), "How it all began – A concise history of Lebanon", A House of Many Mansions – the history of Lebanon reconsidered, I.B. Tauris, ISBN 1-85043-091-8, OCLC 224705916
- Schindler, J (2003), "Steamrollered in Galicia: The Austro-Hungarian Army and the Brusilov Offensive, 1916", War in History, 10 (1): 27–59, doi:10.1191/0968344503wh260oa
- Shanafelt, Gary W (1985), The secret enemy: Austria-Hungary and the German alliance, 1914–1918, East European Monographs, ISBN 978-0-88033-080-0
- Shapiro, Fred R; Epstein, Joseph (2006), The Yale Book of Quotations, Yale University Press, ISBN 0-300-10798-6
- Smith, David James (2010). One Morning In Sarajevo. Hachette UK. ISBN 978-0-297-85608-5.
He was photographed on the way to the station and the photograph has been reproduced many times in books and articles, claiming to depict the arrest of Gavrilo Princip. But there is no photograph of Gavro's arrest – this photograph shows the arrest of Behr.
- Souter, Gavin (2000), Lion & Kangaroo: the initiation of Australia, Melbourne: Text Publishing, OCLC 222801639
- Sisemore, James D (2003), The Russo-Japanese War, Lessons Not Learned, US Army Command and General Staff College
- Smele, Jonathan, "War and Revolution in Russia 1914–1921", World Wars in-depth, BBC, archived from the original on 10 November 2011, retrieved 12 November 2009
- Speed, Richard B, III (1990), Prisoners, Diplomats and the Great War: A Study in the Diplomacy of Captivity, New York: Greenwood Press, ISBN 0-313-26729-4, OCLC 20694547
- Stevenson, David (1996), Armaments and the Coming of War: Europe, 1904–1914, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-820208-3, OCLC 33079190
- Stevenson, David (2004), Cataclysm: The First World War as Political Tragedy, New York: Basic Books, pp. 560pp, ISBN 0-465-08184-3, OCLC 54001282
- Strachan, Hew (2003), The First World War: Volume I: To Arms, New York: Viking, ISBN 0-670-03295-6, OCLC 53075929
- Taylor, Alan John Percivale (1963), The First World War: An Illustrated History, Hamish Hamilton, ISBN 0-399-50260-2, OCLC 2054370
- Taylor, Alan John Percivale (1998), The First World War and its aftermath, 1914–1919, Century of Conflict, 1848–1948, London: Folio Society, OCLC 49988231
- Taylor, John M (Summer 2007), "Audacious Cruise of the Emden", The Quarterly Journal of Military History, 19 (4): 38–47, doi:10.1353/jmh.2007.0331 (inactive 2017-01-15), ISSN 0899-3718
- Terraine, John (1963), Ordeal of Victory, Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott, pp. 508pp, ISBN 0-09-068120-7, OCLC 1345833
- Todman, Dan (4 March 2014). The Great War: Myth and Memory. A & C Black. ISBN 978-0-8264-6728-7.
- Tschanz, David W, Typhus fever on the Eastern front in World War I, Montana State University, retrieved 12 November 2009
- Tuchman, Barbara Wertheim (1966), The Zimmermann Telegram (2nd ed.), New York: Macmillan, ISBN 0-02-620320-0, OCLC 233392415
- Tucker, Spencer C; Roberts, Priscilla Mary (2005), Encyclopedia of World War I, Santa Barbara: ABC-Clio, ISBN 1-85109-420-2, OCLC 61247250
- Tucker, Spencer C; Wood, Laura Matysek; Murphy, Justin D (1999), The European powers in the First World War: an encyclopedia, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0-8153-3351-7
- von der Porten, Edward P (1969), German Navy in World War II, New York: T. Y. Crowell, ISBN 0-213-17961-X, OCLC 164543865
- Westwell, Ian (2004), World War I Day by Day, St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing, pp. 192pp, ISBN 0-7603-1937-5, OCLC 57533366
- Wilgus, William John (1931), Transporting the A. E. F. in Western Europe, 1917–1919, New York: Columbia University Press, OCLC 1161730
- Willmott, H.P. (2003), World War I, New York: Dorling Kindersley, ISBN 0-7894-9627-5, OCLC 52541937
- Winegard, Timothy, "Here at Vimy: A Retrospective – The 90th Anniversary of the Battle of Vimy Ridge", Canadian Military Journal, 8 (2)
- Winter, Denis (1983), The First of the Few: Fighter Pilots of the First World War, Penguin, ISBN 978-0-14-005256-5
- Wohl, Robert (1979), The Generation of 1914 (3 ed.), Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-34466-2
- Zieger, Robert H (2001), America's Great War: World War I and the American experience, Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield, p. 50, ISBN 0-8476-9645-6
- "History in brief (Israel)", The Economist, 28 July 2005, retrieved 30 December 2008
- Israeli Foreign Ministry, Ottoman Rule, Jewish Virtual Library, retrieved 30 December 2008
- De Groot, Gerard J (2001). The First World War. Basingstoke: Palgrave. ISBN 0-333-74534-5.
- Turner, Leonard Charles Frederick (1976). Origins of the First World War. London: Edward Arnold. ISBN 0-393-09947-4.
- Henig, Ruth B. (Ruth Beatrice) (1994). The origins of the First World War. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-10233-2.
- Stevenson, David (1988). The First World War and international politics. Oxford: University Press. ISBN 0-19-873049-7.
Primary sources
- Collins, Ross F. ed. World War I: Primary Documents on Events from 1914 to 1919 (Greenwood Press, 2008) online
Historiography and memory
- Baker, Kevin (June 2006), "Stabbed in the Back! The past and future of a right-wing myth", Harper's Magazine
- Deak, John. "The Great War and the Forgotten Realm: The Habsburg Monarchy and the First World War" Journal of Modern History (2014) 86#2 pp: 336–380.
- Iriye, Akira. "The Historiographic Impact of the Great War." Diplomatic History (July 2014) doi: 10.1093/dh/dhu035
- Jones, Heather. "As the centenary approaches: the regeneration of First World War historiography." Historical Journal (2013) 56#3 pp: 857–878.
- Jones, Heather. "Goodbye to all that?: Memory and meaning in the commemoration of the first world war." Juncture (2014) 20#4 pp: 287–291.
- Kitchen, James E., Alisa Miller and Laura Rowe, eds. Other Combatants, Other Fronts: Competing Histories of the First World War (2011) excerpt
- Kramer, Alan. "Recent Historiography of the First World War – Part I", Journal of Modern European History (Feb. 2014) 12#1 pp 5–27; "Recent Historiography of the First World War (Part II)", (May 2014) 12#2 pp 155–174
- Mulligan, William. "The Trial Continues: New Directions in the Study of the Origins of the First World War." English Historical Review (2014) 129#538 pp: 639–666.
- Reynolds, David. The Long Shadow: The Legacies of the Great War in the Twentieth Century (2014) Excerpt and text search
- Sanborn, Joshua. "Russian Historiography on the Origins of the First World War Since the Fischer Controversy." Journal of Contemporary History (2013) 48#2 pp: 350–362.
- Sharp, Heather. "Representing Australia's Involvement in the First World War: Discrepancies between Public Discourses and School History Textbooks from 1916 to 1936." Journal of Educational Media, Memory, and Society (2014) 6#1 pp: 1–23.
- Trout, Stephen. "On the Battlefield of Memory: The First World War and American Remembrance, 1919–1941 (2013)
- Turan, Ömer. "Turkish Historiography of the First World War." Middle East Critique (2014) 23#2 pp: 241–257.
- Winter, Jay, ed. The Cambridge History of the First World War (2 vol. Cambridge University Press, 2014)
External links
- 1914–1918-online International Encyclopedia of the First World War
- The Heritage of the Great War / First World War. Graphic color photos, pictures and music
- A multimedia history of World War I
- European Newspapers from the start of the First World War and the end of the war
- Powerpoint summary of the war
- The World War I Document Archive Wiki, Brigham Young University
- Maps of Europe covering the history of World War I at omniatlas.com
- "World War I Crossroads" current discussions by scholars
- World War I (First World War) Guide to websites
- Documents from Mount Holyoke College
- EFG1914 – Film digitisation project on First World War
- WWI Films on the European Film Gateway
- The British Pathé WW1 Film Archive
- World War I British press photograph collection – A sampling of images distributed by the British government during the war to diplomats overseas, from the UBC Library Digital Collections
- World War I in Colour in YouTube.
Animated maps
Library guides
Categories:
- World Wars
- World War I
- Modern history of Italy
- French Third Republic
- Global conflicts
- History of Austria-Hungary
- 1910s in Serbia
- History of the United States (1865–1918)
- Russo-Turkish Wars
- Wars involving Armenia
- Wars involving Australia
- Wars involving Azerbaijan
- Wars involving Belgium
- Wars involving Brazil
- Wars involving British India
- Wars involving Bulgaria
- Wars involving Canada
- Wars involving Costa Rica
- Wars involving Cuba
- Wars involving France
- Wars involving Germany
- Wars involving Greece
- Wars involving Guatemala
- Wars involving Haiti
- Wars involving Honduras
- Wars involving Ireland
- Wars involving Italy
- Wars involving Japan
- Wars involving Korea
- Wars involving Liberia
- Wars involving Malta
- Wars involving Montenegro
- Wars involving Nepal
- Wars involving New Zealand
- Wars involving Nicaragua
- Wars involving Panama
- Wars involving Portugal
- Wars involving Rhodesia
- Wars involving Romania
- Wars involving Russia
- Wars involving Serbia
- Wars involving South Africa
- Wars involving Sri Lanka
- Wars involving Sudan
- Wars involving Taiwan
- Wars involving Thailand
- Wars involving the Habsburg Monarchy
- Wars involving the Ottoman Empire
- Wars involving the Republic of China
- Wars involving the states and peoples of Oceania
- Wars involving the United Kingdom
- Wars involving the United States
Following the assassination of Franz Ferdinand in June 1914, Croats and Muslims in Sarajevo joined forces in an anti-Serb pogrom.
... the assassination was followed by officially encouraged anti-Serb riots in Sarajevo ...
... arrested and interned some 5.500 prominent Serbs and sentenced to death some 460 persons, a new Schutzkorps, an auxiliary militia, widened the anti-Serb repression.
The final payment of £59.5 million, writes off the crippling debt that was the price for one world war and laid the foundations for another.
World War I ended over the weekend. Germany made its final reparations-related payment for the Great War on Oct. 3, nearly 92 years after the country's defeat by the Allies.
Germany and the Allies can call it even on World War I this weekend.
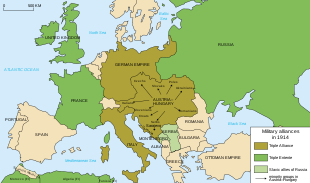




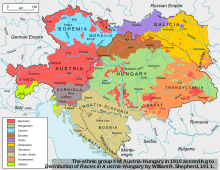
















































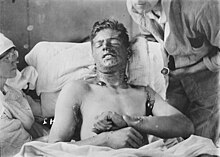





















No comments:
Post a Comment